Here is a selection of data taken from the tables of R74.
|
Year |
Cost per MB in US $ |
Actual memory component |
Speed nsec. |
Memory Type |
|
|
Size (KB) |
Cost (US $) |
||||
|
1957 |
411,041,792.00 |
0.0098 |
392.00 |
10,000 |
transistors |
|
1959 |
67,947,725.00 |
0.0098 |
64.80 |
10,000 |
vacuum tubes |
|
1960 |
5,242,880.00 |
0.0098 |
5.00 |
11,500 |
core |
|
1965 |
2,642,412.00 |
0.0098 |
2.52 |
2,000 |
core |
|
1970 |
734,003.00 |
0.0098 |
0.70 |
770 |
core |
|
1973 |
399,360.00 |
12 |
4680.00 |
?? |
core |
|
1975 |
49,920.00 |
4 |
159.00 |
?? |
static RAM |
|
1976 |
32,000.00 |
8 |
250.00 |
?? |
static RAM |
|
1978 |
10,520.00 |
32 |
475.00 |
?? |
dynamic RAM |
|
1979 |
6,704.00 |
64 |
419.00 |
?? |
dynamic RAM |
|
1981 |
4,479.00 |
64 |
279.95 |
?? |
dynamic RAM |
|
1982 |
1,980.00 |
256 |
495.00 |
?? |
dynamic RAM |
|
1984 |
1,331.00 |
384 |
499.00 |
?? |
dynamic RAM |
|
1985 |
300.00 |
2,048 |
599.00 |
?? |
DRAM |
|
1986 |
190.00 |
3,072 |
528.50 |
?? |
DRAM |
|
1987 |
133.00 |
3,072 |
399.00 |
?? |
DRAM |
|
1989 |
113.00 |
8,192 |
905.00 |
?? |
DRAM |
|
1990 |
46.00 |
1,024 |
45.50 |
80 |
SIMM |
|
1991 |
40.00 |
4,096 |
159.00 |
80 |
SIMM |
|
1992 |
26.30 |
4,096 |
105.00 |
80 |
SIMM |
|
1993 |
35.80 |
4,096 |
143.00 |
70 |
SIMM |
|
1994 |
32.30 |
4,096 |
129.00 |
70 |
SIMM |
|
1995 |
30.90 |
16,384 |
460.00 |
70 |
72 pin SIMM |
|
1996 |
5.25 |
8,192 |
42.00 |
70 |
72 pin SIMM |
|
1997 |
2.16 |
32,768 |
69.00 |
?? |
72 pin SIMM EDO |
|
1998 |
0.84 |
32,768 |
46.00 |
?? |
72 p. SIMM FPM |
|
|
Cost (Cents) |
Size (MB) |
|
Bus Speed |
|
|
1999 |
78¢ |
128 |
99.99 |
?? |
DIMM |
|
2000 |
70¢ |
128 |
89.00 |
133 MHz |
DIMM |
|
2001 |
15¢ |
128 |
18.89 |
133 MHz |
DIMM |
|
2002 |
13¢ |
256 |
34.19 |
133 MHz |
DIMM |
|
2003 |
7.6¢ |
512 |
65.99 |
?? |
DIMM DDR |
|
2004 |
14.6¢ |
512 |
75.00 |
?? |
DIMM DDR |
|
2005 |
11.6¢ |
1,024 |
119.00 |
500 MHz |
DIMM DDR2 |
|
2006 |
7.3¢ |
2,048 |
148.99 |
667 MHz |
DIMM DDR2 |
|
2007 |
2.4¢ |
2,048 |
49.95 |
800 MHz |
DIMM DDR2 |
|
2008 |
1.0¢ |
4,096 |
39.99 |
800 MHz |
DIMM DDR2 |
|
2009 |
1.15¢ |
4,096 |
46.99 |
800 MHz |
DIMM DDR2 |
|
2010 |
1.22¢ |
8192 |
99.99 |
1333 MHz |
DIMM DDR2 |
All terms used in the last two columns of this table will be explained later in this chapter.
Memory as a Linear Array
Consider a byte-addressable memory with N bytes of memory. As stated above, such a memory can be considered to be the logical equivalent of a C++ array, declared as
byte memory[N] ; // Address ranges from 0 through (N – 1)
The computer on which these notes were written has 512 MB of main memory, now only an average size but once unimaginably large. 512 MB = 512·220 bytes = 229 bytes and the memory is byte-addressable, so N = 512·1048576 = 536,870,912.
The term “random access” used when discussing computer memory implies that memory can be accessed at random with no performance penalty. While this may not be exactly true in these days of virtual memory, the key idea is simple – that the time to access an item in memory does not depend on the address given. In this regard, it is similar to an array in which the time to access an entry does not depend on the index. A magnetic tape is a typical sequential access device – in order to get to an entry one must read over all pervious entries.
There are
two major types of random-access computer memory. These are: RAM
(Read-Write Memory) and ROM (Read-Only
Memory). The usage of the term “RAM” for
the type of random access memory that might well be called “RWM” has a long
history and will be continued in this course.
The basic reason is probably that the terms “RAM” and “ROM” can easily
be pronounced; try pronouncing “RWM”.
Keep in mind that both RAM and ROM are random access memory.
Of course, there is no such thing as a pure Read-Only memory; at some time it must be possible to put data in the memory by writing to it, otherwise there will be no data in the memory to be read. The term “Read-Only” usually refers to the method for access by the CPU. All variants of ROM share the feature that their contents cannot be changed by normal CPU write operations. All variants of RAM (really Read-Write Memory) share the feature that their contents can be changed by normal CPU write operations. Some forms of ROM have their contents set at time of manufacture, other types called PROM (Programmable ROM), can have contents changed by special devices called PROM Programmers.
Pure ROM is more commonly found in devices, such as keyboards, that are manufactured in volume, where the cost of developing the chip can be amortized over a large production volume. PROM, like ROM, can be programmed only once. PROM is cheaper than ROM for small production runs, and provides considerable flexibility for design. There are several varieties of EPROM (Erasable PROM), in which the contents can be erased and rewritten many times. There are very handy for research and development for a product that will eventually be manufactured with a PROM, in that they allow for quick design changes.
We now introduce a new term, “shadow RAM”. This is an old concept, going back to the early days of MS–DOS (say, the 1980’s). Most computers have special code hardwired into ROM. This includes the BIOS (Basic Input / Output System), some device handlers, and the start–up, or “boot” code. Use of code directly from the ROM introduces a performance penalty, as ROM (access time about 125 to 250 nanoseconds) is usually slower than RAM (access time 60 to 100 nanoseconds). As a part of the start–up process, the ROM code is copied into a special area of RAM, called the shadow RAM, as it shadows the ROM code. The original ROM code is not used again until the machine is restarted.
Registers associated with the memory system
All memory types, both RAM and ROM can be characterized by
two registers and a number of control signals.
Consider a memory of 2N words, each having M bits. Then
the MAR (Memory Address
Register) is an N-bit register used to specify the
memory address
the MBR (Memory Buffer
Register) is an M-bit register used to hold data to
be written to the
memory or just read from the memory.
This register is
also called the
MDR (Memory Data Register).
We specify the control signals to the memory unit by recalling
what we need the unit to do. First
consider RAM (Read Write Memory). From
the viewpoint of the CPU there are three tasks for the memory CPU reads data from the memory. Memory contents are not changed.
CPU writes data to the memory. Memory contents are updated.
CPU does not access the memory. Memory contents are not changed.
We need two control signals to
specify the three options for a RAM unit.
One standard set is
![]() – the memory
unit is selected. This signal is active
low.
– the memory
unit is selected. This signal is active
low.
![]() – if 0 the CPU
writes to memory, if 1 the CPU reads from memory.
– if 0 the CPU
writes to memory, if 1 the CPU reads from memory.
We can use a truth table to specify the actions for a
RAM. Note that when ![]() = 1,
= 1,
|
|
|
Action |
|
1 |
0 |
Memory contents are not changed. |
|
1 |
1 |
Memory contents are not changed. |
|
0 |
0 |
CPU writes data to the memory. |
|
0 |
1 |
CPU reads data from the memory. |
nothing is happening to the memory. It is not being accessed by the CPU and the
contents do not change. When ![]() = 0, the memory
is active and something happens.
= 0, the memory
is active and something happens.
Consider now a ROM (Read Only Memory). Form the viewpoint of the CPU there are only
two tasks for the memory
CPU reads data from the
memory.
CPU does not access the
memory.
We need only one control signal
to specify these two options. The
natural choice is the ![]() control signal
as the
control signal
as the ![]() signal does not
make sense if the memory cannot be written by the CPU. The truth table for the ROM should be obvious
signal does not
make sense if the memory cannot be written by the CPU. The truth table for the ROM should be obvious
|
|
Action |
|
1 |
CPU is not accessing the memory. |
|
0 |
CPU reads data from the memory. |
In discussing memory, we make two definitions relating to the speed of the memory.
Memory access time is the time required for the memory to access the data; specifically, it is the time between the instant that the memory address is stable in the MAR and the data are available in the MBR. Note that the table above has many access times of 70 or 80 ns. The unit “ns” stands for “nanoseconds”, one–billionth of a second.
Memory cycle time is the minimum time between two independent memory accesses. It should be clear that the cycle time is at least as great as the access time, because the memory cannot process an independent access while it is in the process of placing data in the MBR.
SRAM (Static RAM)
and DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
We now discuss technologies used to store binary information. The first topic is to make a list of requirements for devices used to implement binary memory.
1) Two
well defined and distinct states.
2) The
device must be able to switch states reliably.
3) The
probability of a spontaneous state transition must be extremely low.
4) State
switching must be as fast as possible.
5) The
device must be small and cheap so that large capacity memories are practical.
There are a number of memory technologies that were developed in the last half of the twentieth century. Most of these are now obsolete. There are three that are worth mention:
1) Core Memory (now obsolete, but new
designs may be introduced soon)
2) Static RAM
3) Dynamic RAM
Each of static RAM and dynamic
RAM may be considered to be a semiconductor memory. As such, both types are volatile, in that
they lose their contents when power is shut off. Core
memory is permanent; it will retain its contents even when not under
power.
Core Memory
This was a major advance when it was introduced in 1952, first used on the MIT Whirlwind. The basic memory element is a torus (tiny doughnut) of magnetic material. This torus can contain a magnetic field in one of two directions. These two distinct directions allow for a two-state device, as required to store a binary number. Core memory is no longer used.
There is a modern variant of core memory, called “MRAM” for Magnetoresistive RAM that has caused some interest recently. It is a non–volatile magnetic memory that has been in development since the 1990’s. In 2003, there was a report [R95] that IBM had produced a 128 kb (kilobit) chip with write/read access time approximately 2 nanoseconds, which is better than most SRAM. In April 2011 [R76], 4Mb MRAM chips, with an access time of 35 nanoseconds, were available for about $21. At $20/megabyte, this is about three orders of magnitude more expensive than standard DRAM, but 2 or 3 times as fast.
One aspect of magnetic core memory remains with us – the frequent use of the term “core memory” as a synonym for the computer’s main memory.
Static RAM
Static RAM (SRAM) is a memory technology based on flip-flops. SRAM has an access time of 2 – 10 nanoseconds. From a logical view, all of main memory can be viewed as fabricated from SRAM, although such a memory would be unrealistically expensive.
Dynamic RAM
Dynamic RAM (DRAM) is a memory technology based on capacitors – circuit elements that store electronic charge. Dynamic RAM is cheaper than static RAM and can be packed more densely on a computer chip, thus allowing larger capacity memories. DRAM has an access time in the order of 60 – 100 nanoseconds, slower than SRAM.
Multi–level memory systems combine SRAM, DRAM, and disk memory to produce a large memory with reasonable effective access times. We discuss these topics later in this chapter.
The Idea of Address
Space
We now must distinguish between the idea of address space and physical memory. The address space defines the range of addresses (indices into the memory array) that can be generated. The size of the physical memory is usually somewhat smaller, this may be by design (see the discussion of memory-mapped I/O below) or just by accident. The standard variants in use as of 2011 are 32–bit and 64–bit address spaces. One hears of 32–bit versions and 64–bit versions of MS–Windows; the names indicate the address spaces used.
An N–bit address will specify 2N different addresses. In this sense, the address can be viewed as an N–bit unsigned integer; the range of which is 0 to 2N – 1 inclusive. We can ask another question: given M addressable items, how many address bits are required. The answer is given by the equation 2(N - 1) < M £ 2N, which is best solved by guessing N.
The memory address is specified by a binary number placed in the Memory Address Register (MAR). The number of bits in the MAR determines the range of addresses that can be generated. N address lines can be used to specify 2N distinct addresses, numbered 0 through 2N – 1. This is called the address space of the computer.
For example, we show three MAR sizes.
Computer |
MAR bits |
|
|
PDP-11/20 |
16 |
0 to 65 535 |
|
Intel 8086 |
20 |
0 to 1 048 575 |
|
Intel Pentium |
32 |
0 to 4 294 967 295 |
The PDP-11/20 was an elegant small machine made by the now defunct Digital Equipment Corporation. As soon as it was built, people realized that its address range was too small.
In general, the address space is much larger than the physical memory available. For example, my personal computer has an address space of 232 (as do all Pentiums), but only 384MB = 228 + 227 bytes. Until recently the 32–bit address space would have been much larger than any possible amount of physical memory. At present one can go to a number of companies and order a computer with a fully populated address space; i.e., 4 GB of physical memory. Most high-end personal computers are shipped with 1GB of memory.
In a design with memory-mapped I/O part of the address space is dedicated to
addressing I/O registers and not physical memory. For example, in the original PDP–11/20, the
top 4096 (212) of the address space was dedicated to I/O registers,
leading to the memory map.
Addresses 0 – 61439 Available for physical memory
Addresses 61440 – 61535 Available for I/O registers (61440 = 61536 –
4096)
Word Addresses in a
Byte-Addressable Machine
Most
computers today have memories that are byte-addressable; thus each byte
in the memory has a unique address that can be used to address it. Under this addressing scheme, a word
corresponds to a number of addresses.
A 16–bit word at address Z contains
bytes at addresses Z and Z + 1.
A 32–bit word at address Z contains
bytes at addresses Z, Z + 1, Z + 2, and Z + 3.
In many
computers with byte addressing, there are constraints on word addresses.
A 16–bit word must have an even
address
A 32–bit word must have an address
that is a multiple of 4.
Even in computers that do not enforce this requirement, it is a good idea to observe these word boundaries. Most compilers will do so automatically.
Suppose a
byte-addressable computer with a 32-bit address space. The highest byte address is 232 –
1. From this fact and the address
allocation to multi-byte words, we conclude
the highest address for a 16-bit
word is (232 – 2), and
the highest address for a 32-bit word is (232 – 4), because the 32-bit word addressed at (232 – 4) comprises bytes at addresses (232 – 4), (232 – 3), (232 – 2), and (232 – 1).
Byte Addressing vs. Word Addressing
We have noted above that N address lines can be used to specify 2N distinct addresses, numbered 0 through 2N – 1. We now ask about the size of the addressable items. We have seen that most modern computers are byte-addressable; the size of the addressable item is therefore 8 bits or one byte. There are other possibilities. We now consider the advantages and drawbacks of having larger entities being addressable.
As a simple example, consider a computer with a 16–bit address space. The machine would have 65,536 (64K = 216) addressable entities. The maximum memory size would depend on the size of the addressable entity.
Byte Addressable 64 KB
16-bit Word Addressable 128 KB
32-bit Word Addressable 256 KB
For a given
address space, the maximum memory size is greater for the larger addressable
entities. This may be an advantage for
certain applications, although this advantage is reduced by the very large
address spaces we now have: 32–bits is common and 64–bit
address spaces are easily available. The
sizes of these address spaces are quite large.
32–bit address space 4, 294, 967, 296 bytes (4 gigabytes)
64–bit address space about 1.8467·1019
bytes 16 billion gigabytes.
The advantages of byte-addressability are clear when we consider applications that process data one byte at a time. Access of a single byte in a byte-addressable system requires only the issuing of a single address. In a 16–bit word addressable system, it is necessary first to compute the address of the word containing the byte, fetch that word, and then extract the byte from the two-byte word. Although the processes for byte extraction are well understood, they are less efficient than directly accessing the byte. For this reason, many modern machines are byte addressable.
Big-Endian and Little-Endian
The reference here is to a story in Gulliver’s Travels written by Jonathan Swift in which two groups of men went to war over which end of a boiled egg should be broken – the big end or the little end. The student should be aware that Swift did not write pretty stories for children but focused on biting satire; his work A Modest Proposal is an excellent example.
Consider
the 32–bit number represented by the eight–digit hexadecimal number 0x01020304,
stored at location Z in memory. In all
byte-addressable memory locations, this number will be stored in the four
consecutive addresses Z, (Z + 1), (Z + 2), and (Z + 3). The difference between big-endian and
little-endian addresses is where each of the four bytes is stored. In our example 0x01 represents bits 31 – 24, 0x02 represents bits 23 – 16,
0x03 represents
bits 15 – 8, and 0x04 represents
bits 7 – 0 of the word.
As a 32-bit
signed integer, the number 0x01020304 can be represented in decimal notation as
1·166
+ 0·165
+ 2·164
+ 0·163
+ 3·162
+ 0·161
+ 4·160
= 16,777,216 + 131,072 + 768 + 4 = 16,909,060.
For those who like to think in bytes, this is (01)·166
+ (02)·164
+ (03)·162
+ 04, arriving at the same result. Note
that the number can be viewed as having a “big end” and a “little end”, as in
the following figure.
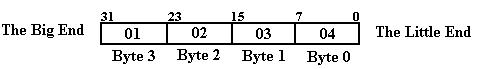
The “big end” contains the most significant digits of the number and the “little end” contains the least significant digits of the number. We now consider how these bytes are stored in a byte-addressable memory. Recall that each byte, comprising two hexadecimal digits, has a unique address in a byte-addressable memory, and that a 32-bit (four-byte) entry at address Z occupies the bytes at addresses Z, (Z + 1), (Z + 2), and (Z + 3). The hexadecimal values stored in these four byte addresses are shown below.
Address Big-Endian Little-Endian
Z 01 04
Z + 1 02 03
Z + 2 03 02
Z + 3 04 01
Just to be complete, consider the 16–bit number represented by the four hex digits 0A0B. Suppose that the 16-bit word is at location W; i.e., its bytes are at locations W and (W + 1). The most significant byte is 0x0A and the least significant byte is 0x0B. The values in the two addresses are shown below.
Address Big-Endian Little-Endian
W 0A 0B
W + 1 0B 0A
The figure below shows a graphical way to view these two options for ordering the bytes copied from a register into memory. We suppose a 32-bit register with bits numbered from 31 through 0. Which end is placed first in the memory – at address Z? For big-endian, the “big end” or most significant byte is first written. For little-endian, the “little end” or least significant byte is written first.
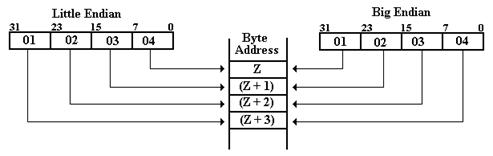
There seems to be no advantage of one system over the other. Big–endian seems more natural to most people and facilitates reading hex dumps (listings of a sequence of memory locations), although a good debugger will remove that burden from all but the unlucky.
Big-endian computers include the IBM 360 series, Motorola 68xxx, and SPARC by Sun.
Little-endian computers include the Intel Pentium and related computers.
The big-endian vs. little-endian debate is one that does not concern most of us directly. Let the computer handle its bytes in any order desired as long as it produces good results. The only direct impact on most of us will come when trying to port data from one computer to a computer of another type. Transfer over computer networks is facilitated by the fact that the network interfaces for computers will translate to and from the network standard, which is big-endian. The major difficulty will come when trying to read different file types.
The big-endian vs. little-endian debate shows in file structures when computer data are “serialized” – that is written out a byte at a time. This causes different byte orders for the same data in the same way as the ordering stored in memory. The orientation of the file structure often depends on the machine upon which the software was first developed.
The
following is a partial list of file types taken from a textbook once used by
this author.
Little-endian Windows BMP, MS Paintbrush, MS RTF, GIF
Big-endian Adobe Photoshop, JPEG, MacPaint
Some applications support both orientations, with a flag in the header record indicating which is the ordering used in writing the file.
Any student who is interested in the literary antecedents of the terms “big-endian” and “little-endian” may find a quotation at the end of this chapter.
Logical View of Memory
As often is the case, we utilize a number of logical models of our memory system, depending on the point we want to make. The simplest view of memory is that of a monolithic linear memory; specifically a memory fabricated as a single unit (monolithic) that is organized as a singly dimensioned array (linear). This is satisfactory as a logical model, but it ignores very many issues of considerable importance.
Consider a memory in which an M–bit
word is the smallest addressable unit.
For simplicity, we assume that the memory contains N = 2K
words and that the address space is also N = 2K. The memory can be viewed as a one-dimensional
array, declared something like
Memory : Array [0 .. (N – 1)]
of M–bit word.
The monolithic view of the memory is shown in the following figure.
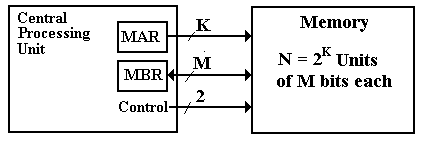
Figure: Monolithic View of Computer Memory
In this monolithic view, the CPU provides K address bits to access N = 2K memory entries, each of which has M bits, and at least two control signals to manage memory.
The linear view of memory is a way to think logically about the organization of the memory. This view has the advantage of being rather simple, but has the disadvantage of describing accurately only technologies that have long been obsolete. However, it is a consistent model that is worth mention. The following diagram illustrates the linear model.
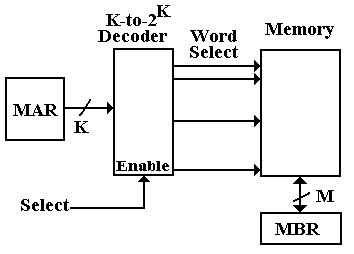
There are two problems with the above model, a minor
nuisance and a “show–stopper”.
The minor problem is the speed of the memory; its access time will be exactly
that of plain variety DRAM (dynamic random access memory), which is
at best 50 nanoseconds. We must have
better performance than that, so we go to other memory organizations.
The “show–stopper” problem is the design of the memory
decoder. Consider two examples for
common memory sizes: 1MB (220 bytes) and 4GB (232 bytes)
in a byte–oriented memory.
A 1MB memory would use a
20–to–1,048,576 decoder, as 220 = 1,048,576.
A 4GB memory would use a
32–to–4,294,967,296 decoder, as 232 = 4,294,967,296.
Neither of these decoders can be
manufactured at acceptable cost using current technology.
At this point, it will be helpful to divert from the main narrative and spend
some time in reviewing the structure of decoders. We shall use this to illustrate the problems
found when attempting to construct large decoders. In particular, we note that larger decoders
tend to be slower than smaller ones. As
a result, larger memories tend to be slower than smaller ones. We shall see why this is the case, and how
that impacts cache design, in particular.
Interlude: The Structure and Use
of Decoders
For the sake of simplicity (and mainly because the figure has already been drawn, and appears in an earlier chapter), we use a 2–to–4 enabled high, active–high decoder as an example. The inferences from this figure can be shown to apply to larger decoders, both active–high and active–low, though the particulars of active–low decoders differ a bit.
An N–to–2N active–high decoder has N inputs, 2N outputs, and 2N N–input AND gates. The corresponding active–low decoder would have 2N N–input OR gates. Each of the N inputs to either design will drive 2N–1 + 1 output gates. As noted above, a 1M memory would require a 20–to–1,048,576 decoder, with 20–input output gates and each input driving 524,899 gates. This seems to present a significant stretch of the technology. On the positive side, the output is available after two gate delays.
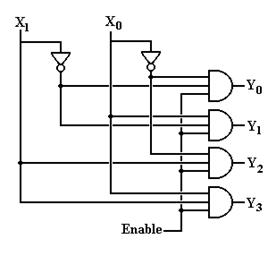
Figure: Sample Decoder Structure
There is another way to handle this, use multiple levels of decoders. To illustrate this, consider the use of 2–to–4 decoders to build a 4–to–16 decoder.
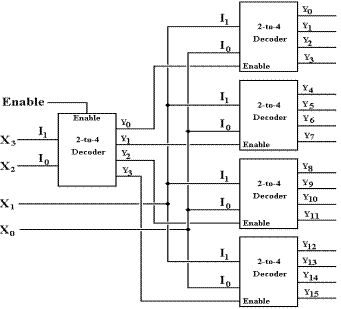
Here, each level of decoder adds two gate delays to the total delay in placing the output. For this example, the output is available 4 gate delays after the input is stable. We now investigate the generalization of this design strategy to building large decoders.
Suppose that 8–to–256 (8–to–28) decoders, with output delays of 2 gate delays, were stock items. A 1MB memory, using a 20–to–1,048,576 (20–to–220) decoder, would require three layers of decoders: one 4–to–16 (4–to–24) decoder and two 8–to–256 (8–to–28) decoders. For this circuit, the output is stable six gate delays after the input is stable.
A 4GB memory using a 32–to–4,294,967,296 (32–to–232) decoder, would require four levels of 8–to–256 (8–to–28) decoders. For this circuit, the output is stable eight gate delays after the input is stable. While seemingly fast, this does slow a memory.
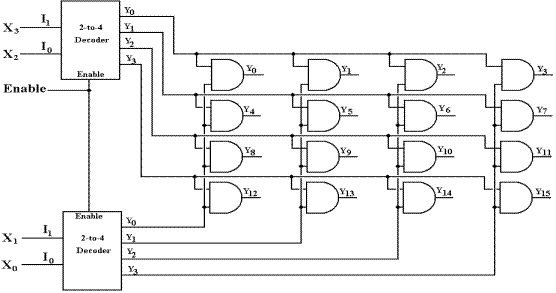
There is a slight variant of
the decoder that suggests a usage found in modern memory designs. It is presented here just to show that this
author knows about it. This figure
generalizes to fabrication of an N–to–2N from two (N/2)–to–2N/2
decoders. In this design, a 1MB memory,
using a 20–to–1,048,576 (20–to–220) decoder, would require two
decoders, each being 10–to–1,024 (10–to–210) and a 4GB memory using
a 32–to–4,294,967,296
(32–to–232) decoder, would require two decoders, each being
16–to–65,536 (16–to–216).
The Physical View of Memory
We now examine two design choices that produce easy-to-manufacture solutions that offer acceptable performance at reasonable price. The first design option is to change the structure of the main DRAM memory. While not obvious in the price chart at the beginning of the chapter, the basic performance of DRAM chips has not changed since the early 1990s’; the basic access time is in the 50 to 80 nanosecond range, with 70 nanoseconds being typical. The second design option is to build a memory hierarchy, using various levels of cache memory, offering faster access to main memory. As mentioned above, the cache memory will be faster SRAM, while the main memory will be slower DRAM.
In a multi–level memory that uses cache memory, the goal in designing the primary memory is to have a design that keeps up with the cache closest to it, and not necessarily the CPU. All modern computer memory is built from a collection of memory chips. This design allows an efficiency boost due to the process called “memory interleaving”.
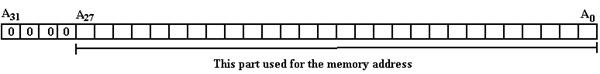
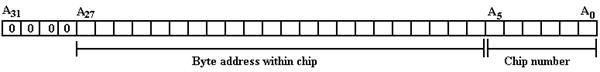
Suppose a
computer with byte-addressable memory, a 32–bit address space, and 256 MB
(228 bytes) of memory. Such a
computer is based on this author’s personal computer, with the memory size
altered to a power of 2 to make for an easier example. The addresses in the MAR can be viewed as 32–bit
unsigned integers, with high order bit A31 and low order bit A0. Putting aside issues of virtual addressing
(important for operating systems), we specify that only 28-bit addresses are
valid and thus a valid address has the following form.
Later in this chapter, we shall investigate a virtual memory system that uses 32–bit addresses mapped to 28–bit physical addresses. For this discussion, we focus on the physical memory.
Here is a depiction of a 32–bit address, in which the lower order 28 bits are used to reference addresses in physical memory.
The memory of all modern computers
comprises a number of chips, which are combined to cover the range of
acceptable addresses. Suppose, in our
example, that the basic memory chips are 4MB chips. The 256 MB memory would be built from 64
chips and the address space divided as follows:
6 bits to select the memory chip as
26 = 64, and
22 bits to select the byte within
the chip as 222 = 4·220 = 4M.
The
question is which bits select the chip and which are sent to the chip. Two options commonly used are high-order memory interleaving and low-order memory interleaving. Other options exist, but the resulting
designs would be truly bizarre. We shall
consider only low-order memory interleaving in which the low-order address bits
are used to select the chip and the higher-order bits select the byte. The advantage of low–order interleaving over
high–order interleaving will be seen when we consider the principle of
locality.
This low-order interleaving has a number
of performance-related advantages. These
are due to the fact that consecutive bytes are stored in different chips, thus
byte 0 is in chip 0, byte 1 is in chip 1, etc.
In our example
Chip 0 contains bytes 0, 64, 128, 192, etc., and
Chip 1 contains bytes 1, 65, 129, 193, etc., and
Chip 63 contains bytes 63, 127, 191, 255, etc.
Suppose
that the computer has a 64 bit–data bus from the memory to the CPU. With the above low-order interleaved memory
it would be possible to read or write eight bytes at a time, thus giving rise
to a memory that is close to 8 times faster.
Note that there are two constraints on the memory performance increase
for such an arrangement.
1) The
number of chips in the memory – here it is 64.
2) The
width of the data bus – here it is 8, or 64 bits.
In this design, the chip count matches the bus width; it is a balanced design.
To anticipate a later discussion, consider the above memory as connected to a cache memory that transfers data to and from the main memory in 64–bit blocks. When the CPU first accesses an address, all of the words (bytes, for a byte addressable memory) in that block are copied into the cache. Given the fact that there is a 64–bit data bus between the main DRAM and the cache, the cache can be very efficiently loaded. We shall have a great deal to say about cache memory later in this chapter.
A design implementing the address scheme just discussed might use a 6–to–64 decoder, or a pair of 3–to–8 decoders to select the chip. The high order bits are sent to each chip and determine the location within the chip. The next figure suggests the design.
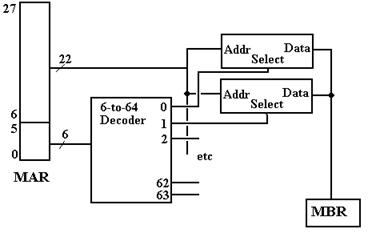
Figure: Partial Design of the Memory Unit
Note that each of the 64 4MB–chips receives the high order bits of the address. At most one of the 64 chips is active at a time. If there is a memory read or write operation active, then exactly one of the chips will be selected and the others will be inactive.
A Closer Look at the Memory “Chip”
So far in our design, we have been able to reduce the problem of creating a 32–to–232 decoder to that of creating a 22–to–222 decoder. We have gained the speed advantage allowed by interleaving, but still have that decoder problem. We now investigate the next step in memory design, represented by the problem of creating a workable 4MB chip.
The answer that we shall use involves creating the chip with eight 4Mb (megabit) chips. The design used is reflected in the figures below.
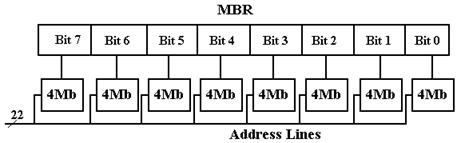
Figure: Eight Chips, each holding 4 megabits, making a 4MB “Chip”
There is an immediate advantage to having one chip represent only one bit in the MBR. This is due to the nature of chip failure. If one adds a ninth 4Mb chip to the mix, it is possible to create a simple parity memory in which single bit errors would be detected by the circuitry (not shown) that would feed the nine bits selected into the 8-bit memory buffer register.
A larger advantage is seen when we notice the decoder circuitry used in the 4Mb chip. It is logically equivalent to the 22–to–4194304 decoder that we have mentioned, but it is built using two 11–to–2048 decoders; these are at least not impossible to fabricate.
Think of the 4194304 (222) bits in the 4Mb chip as being arranged in a two dimensional array of 2048 rows (numbered 0 to 2047), each of 2048 columns (also numbered 0 to 2047). What we have can be shown in the figure below.
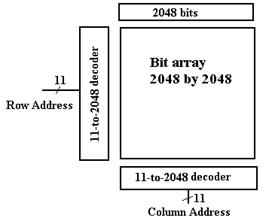
Figure: Memory with Row and Column Addresses
We now add one more feature, to be elaborated below, to our
design and suddenly we have a really fast DRAM chip. For ease of chip manufacture, we split the 22–bit
address into an
11–bit row address and an 11–bit column address. This allows the chip to have only 11 address
pins, with two extra control (RAS and CAS – 14 total) rather than 22 address
pins with an additional select (23 total).
This makes the chip less expensive to manufacture.

Pin Count Address Lines 22 11
Row/Column 0 2
Power & Ground 2 2
Data 1 1
Control 3 3
Total 28 19
Separate row and column addresses require two cycles to specify the address.
We send the 11–bit row address
first and then send the 11–bit column address.
At first sight, this may seem less efficient than sending 22 bits at a
time, but it allows a true speed–up. We
merely add a 2048–bit row buffer onto the chip and when a row is selected; we
transfer all 2048 bits in that row to the buffer at one time. The column select then selects from this
on–chip buffer. Thus, our access time
now has two components:
1) The time to select a new row, and
2) The time to copy a selected bit from a row in the buffer.
This design is the basis for all modern computer memory architectures.
Commercial Memory Chips
As mentioned above, primary memory in commercial computers is fabricated from standard modules that fit onto the motherboard, to which all components of the computer are connected, either directly or (as in the case of disk drives) through flexible cables. The standard memory modules are designed to plug directly into appropriately sized sockets on the motherboard. There are two main types of memory modules: SIMM and DIMM.
SIMM (Single In–Line Memory Module) cards have 72 connector pins in a single row (hence the “single in–line”) and are limited in size to 64 MB.
DIMM (Dual In–Line Memory Module) cards standardly have 168 connector pins in two rows. As of 2011, a 240–pin DIMM module with 1GB capacity was advertised on Amazon.
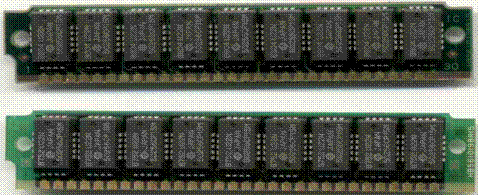
Here is a picture of a SIMM card. It has 60 connectors, arranged in two rows of 30. It appears to be parity memory, as we see nine chips on each side of the card. That is one chip for each of the data bits, and a ninth chip for the parity bit for each 8–bit byte.
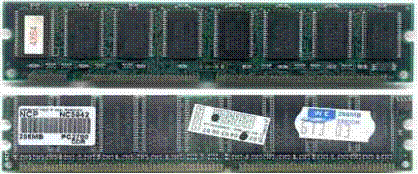
Here is a picture of a DIMM card. It appears to be an older card, with only 256
MB
capacity. Note the eight chips; this has
no parity memory.
SDRAM – Synchronous Dynamic Random
Access Memory
As we mentioned above, the relative slowness of memory as compared to the CPU has long been a point of concern among computer designers. One recent development that is used to address this problem is SDRAM – synchronous dynamic access memory.
The
standard memory types we have discussed up to this point are
SRAM Static Random Access Memory
Typical access
time: 5 – 10 nanoseconds
Implemented with 6
transistors: costly and fairly large.
DRAM Dynamic Random Access Memory
Typical access
time: 50 – 70 nanoseconds
Implemented with
one capacitor and one transistor: small and cheap.
In a way, the desirable approach would be to make the entire memory to be SRAM. Such a memory would be about as fast as possible, but would suffer from a number of setbacks, including very large cost (given current economics a 256 MB memory might cost in excess of $20,000) and unwieldy size. The current practice, which leads to feasible designs, is to use large amounts of DRAM for memory. This leads to an obvious difficulty.
1) The
access time on DRAM is almost never less than 50 nanoseconds.
2) The
clock time on a moderately fast (2.5 GHz) CPU is 0.4 nanoseconds,
125 times faster than the
DRAM.
The
problem that arises from this speed mismatch is often called the “Von Neumann
Bottleneck” – memory cannot supply the CPU at a sufficient data rate. Fortunately there have been a number of
developments that have alleviated this problem.
We will soon discussed the idea of cache
memory, in which a large memory with a 50 to 100 nanosecond access time can
be coupled with a small memory with a 10 nanosecond access time. While
cache memory does help, the main problem is that main memory is too slow.
In
his 2010 book [R06], William Stallings introduced his section on advanced DRAM
organization (Section 5.3, pages 173 to 179) with the following analysis of
standard memory
technology, which I quote verbatim.
“As discussed in Chapter 2 [of the reference], one of the most critical system bottlenecks when using high–performance processors is the interface to main internal memory. This interface is the most important pathway in the entire computer system. The basic building block of memory remains the DRAM chip, as it has for decades; until recently, there had been no significant changes in DRAM architecture since the early 1970s. The traditional DRAM chip is constrained both by its internal architecture and by its interface to the processor’s memory bus.”
Modern computer designs, in an effort to avoid the Von Neumann bottleneck, use several tricks, including multi–level caches and DDR SDRAM main memory. We continue to postpone the discussion of cache memory, and focus on methods to speed up the primary memory in order to make it more compatible with the faster, and more expensive, cache.
Many of the modern developments in memory technology involve Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory, SDRAM for short. Although we have not mentioned it, earlier memory was asynchronous, in that the memory speed was not related to any external speed. In SDRAM, the memory is synchronized to the system bus and can deliver data at the bus speed. The earlier SDRAM chips could deliver one data item for every clock pulse; later designs called DDR SDRAM (for Double Data Rate SDRAM) can deliver two data items per clock pulse. Double Data Rate SDRAM (DDR–SDRAM) doubles the bandwidth available from SDRAM by transferring data at both edges of the clock.
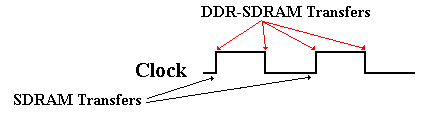
Figure: DDR-SDRAM Transfers Twice as Fast
As an example, we quote from the
Dell Precision T7500 advertisement of June 30, 2011. The machine supports dual processors, each
with six cores. Each of the twelve cores
has two 16 KB L1 caches (an Instruction Cache and a Data Cache) and a 256 KB
(?) L2 cache. The processor pair shares
a 12 MB Level 3 cache. The standard
memory configuration calls for
4GB or DDR3 memory, though the system will support up to 192 GB. The memory bus operates at 1333MHz (2666
million transfers per second). If it has
64 data lines to the L3 cache (following the design of the Dell Dimension 4700
of 2004), this corresponds to
2.666·109
transfers/second ·
8 bytes/transfer »
2.13·1010
bytes per second. This is a peak
transfer rate of 19.9 GB/sec.
The SDRAM chip uses a number of tricks to deliver data at an acceptable rate. As an example, let’s consider a modern SDRAM chip capable of supporting a DDR data bus. In order to appreciate the SDRAM chip, we must begin with simpler chips and work up.
We
begin with noting an approach that actually imposes a performance hit – address
multiplexing. Consider an NTE2164, a
typical 64Kb chip. With 64K of
addressable units, we would expect 16 address lines, as 64K = 216. In stead we find 8 address lines and two
additional control lines
![]() Row Address Strobe (Active Low)
Row Address Strobe (Active Low)
![]() Column Address Strobe (Active Low)
Column Address Strobe (Active Low)
Here is how it works. Recalling that 64K = 216 = 28 · 28 = 256 · 256, we organize the memory as a 256-by-256 square array. Every item in the memory is uniquely identified by two addresses – its row address and its column address.
Here is the way that the 8-bit address is interpreted.
|
|
|
Action |
|
0 |
0 |
An error – this had better not happen. |
|
0 |
1 |
It is a row address (say the high order 8-bits of the 16-bit address) |
|
1 |
0 |
It is a column address (say the low order 8-bits of the 16-bit address) |
|
1 |
1 |
It is ignored. |
Here is that way that the NTE2164
would be addressed.
1) Assert
![]() = 0 and place
the A15 to A8 on the 8–bit address bus.
= 0 and place
the A15 to A8 on the 8–bit address bus.
2) Assert
![]() = 0 and place A7
to A0 on the 8–bit address bus.
= 0 and place A7
to A0 on the 8–bit address bus.
There
are two equivalent design goals for such a design.
1) To
minimize the number of pins on the memory chip.
We have two options:
8 address pins,
RAS, and CAS (10 pins), or
16 address pins
and an Address Valid pin (17 pins).
2) To
minimize the number of address–related lines on the data bus.
The same numbers
apply here: 10 vs. 17.
With this design in mind, we are able to consider the next step in memory speed-up. It is called Fast-Page Mode DRAM, or FPM–DRAM.
Fast-Page Mode DRAM implements page mode, an improvement on conventional DRAM in which the row-address is held constant and data from multiple columns is read from the sense amplifiers. The data held in the sense amps form an “open page” that can be accessed relatively quickly. This speeds up successive accesses to the same row of the DRAM core.
The move from FPM–DRAM to SDRAM is logically just making the DRAM interface synchronous to the data bus in being controlled by a clock signal propagated on that bus. The design issues are now how to create a memory chip that can respond sufficiently fast. The underlying architecture of the SDRAM core is the same as in a conventional DRAM. SDRAM transfers data at one edge of the clock, usually the leading edge.
So far, we have used a SRAM memory as a L1 cache to speed up effective memory access time and used Fast Page Mode DRAM to allow quick access to an entire row from the DRAM chip. We continue to be plagued with the problem of making the DRAM chip faster. If we are to use the chip as a DDR–SDRAM, we must speed it up quite a bit.
Modern DRAM designs are increasing the amount of SRAM on the DRAM die. In most cases a memory system will have at least 8KB of SRAM on each DRAM chip, thus leading to the possibility of data transfers at SRAM speeds.
We
are now faced with two measures: latency and bandwidth.
Latency is the amount of time for
the memory to provide the first element of a block
of contiguous data.
Bandwidth is the rate at which the
memory can deliver data once the row address
has been accepted.
One can increase the bandwidth of memory by making the data bus “wider” – that is able to transfer more data bits at a time. It turns out that the optimal size is half that of a cache line in the L2 cache. Now – what is a cache line?
In order to understand the concept of a cache line, we must return to our discussion of cache memory. What happens when there is a cache miss on a memory read? The referenced byte must be retrieved from main memory. Efficiency is improved by retrieving not only the byte that is requested, but also a number of nearby bytes.
Cache memory is organized into cache lines. Suppose that we have a L2 cache with a cache line size of 16 bytes. Data could be transferred from main memory into the L2 cache in units of 8 or 16 bytes. This depends on the size of the memory bus; 64 or 128 bits.
Suppose that the byte with address 0x124A is requested and found not to be in the L2 cache. A cache line in the L2 cache would be filled with the 16 bytes with addresses ranging from 0x1240 through 0x124F. This might be done in two transfers of 8 bytes each.
We
close this part of the discussion by examining some specifications of a memory
chip that as of July 2011 seemed to be state-of-the-art. This is the Micron DDR2 SDRAM in 3 models
MT46H512M4 64 MEG x 4 x 8 banks
MT47H256M8 32 MEG x 8 x 8 banks
MT47H128M16 16 MEG x 16 x 8 banks
Collectively, the memories are described by Micron [R89] as “high-speed dynamic random–access memory that uses a 4ns–prefetch architecture with an interface designed to transfer two data words per clock cycle at the I/O bond pads.” But what is “prefetch architecture”?
According to Wikipedia [R90]
“The prefetch buffer takes advantage of the specific characteristics of memory accesses to a DRAM. Typical DRAM memory operations involve three phases (line precharge, row access, column access). Row access is … the long and slow phase of memory operation. However once a row is read, subsequent column accesses to that same row can be very quick, as the sense amplifiers also act as latches. For reference, a row of a 1Gb DDR3 device is 2,048 bits wide, so that internally 2,048 bits are read into 2,048 separate sense amplifiers during the row access phase. Row accesses might take 50 ns depending on the speed of the DRAM, whereas column accesses off an open row are less than 10 ns.”
“In a prefetch buffer architecture, when a memory access occurs to a row the buffer grabs a set of adjacent datawords on the row and reads them out ("bursts" them) in rapid-fire sequence on the IO pins, without the need for individual column address requests. This assumes the CPU wants adjacent datawords in memory which in practice is very often the case. For instance when a 64 bit CPU accesses a 16 bit wide DRAM chip, it will need 4 adjacent 16 bit datawords to make up the full 64 bits. A 4n prefetch buffer would accomplish this exactly ("n" refers to the IO width of the memory chip; it is multiplied by the burst depth "4" to give the size in bits of the full burst sequence).”
“The prefetch buffer depth can also be thought of as the ratio between the core memory frequency and the IO frequency. In an 8n prefetch architecture (such as DDR3), the IOs will operate 8 times faster than the memory core (each memory access results in a burst of 8 datawords on the IOs). Thus a 200 MHz memory core is combined with IOs that each operate eight times faster (1600 megabits/second). If the memory has 16 IOs, the total read bandwidth would be 200 MHz x 8 datawords/access x 16 IOs = 25.6 gigabits/second (Gbps), or 3.2 gigabytes/second (GBps). Modules with multiple DRAM chips can provide correspondingly higher bandwidth.”
Each is compatible with 1066 MHz synchronous operation at double data rate. For the MT47H128M16 (16 MEG x 16 x 8 banks, or 128 MEG x 16), the memory bus can apparently be operated at 64 times the speed of internal memory; hence the 1066 MHz.
Here is a functional block diagram of the 128 Meg x 16 configuration, taken from the Micron reference [R91]. Note that there is a lot going on inside that chip.
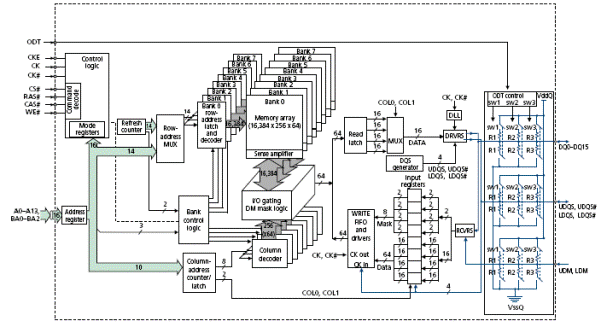
Here are the important data and address lines to the memory chip.
A[13:0] The address inputs; either row address or column address.
DQ[15:0] Bidirectional data input/output lines for the memory chip.
A few
of these control signals are worth mention.
Note that most of the control signals are
active–low; this is denoted in the modern notation by the sharp sign.
CS# Chip
Select. This is active low, hence the
“#” at the end of the signal name.
When low, this enables
the memory chip command decoder.
When high, is disables
the command decoder, and the chip is idle.
RAS# Row Address Strobe. When enabled, the address refers to the row number.
CAS# Column Address Strobe. When enabled, the address refers to the column
WE# Write Enable. When enabled, the CPU is writing to the memory.
The following truth table explains the operation of the chip.
|
CS# |
RAS# |
CAS# |
WE# |
Command / Action |
|
1 |
d |
d |
d |
Deselect / Continue previous operation |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
NOP / Continue previous operation |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
Select and activate row |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
Select column and start READ burst |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Select column and start WRITE burst |
The Cache Model
The next figure shows a simple memory hierarchy, sufficient to illustrate the two big ideas about multi–level memory: cache memory and virtual memory.
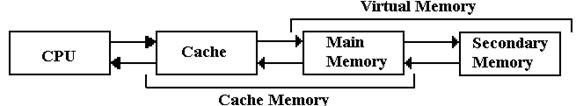
Figure: The Memory Hierarchy with Cache and Virtual Memory
We consider a multi-level memory system as having a faster primary memory and a slower secondary memory. In cache memory, the cache is the faster primary memory and the main memory is the secondary memory. We shall ignore virtual memory at this point.
Program Locality: Why Does A
Cache Work?
The design goal for cache memory is to create a memory unit with the performance of SRAM, but the cost and packaging density of DRAM. In the cache memory strategy, a fast (but small) SRAM memory fronts for a larger and slower DRAM memory. The reason that this can cause faster program execution is due to the principle of locality, first discovered by Peter J. Denning as part of his research for his Ph.D. The usual citation for Denning’s work on program locality is his ACM paper [R78].
The basic idea behind program locality is the observed behavior of memory references; they tend to cluster together within a small range that could easily fit into a small cache memory. There are generally considered to be two types of locality. Spatial locality refers to the tendency of program execution to reference memory locations that are clustered; if this address is accessed, then one very near it will be accessed soon. Temporal locality refers to the tendency of a processor to access memory locations that have been accessed recently. In the less common case that a memory reference is to a “distant address”, the cache memory must be loaded from another level of memory. This event, called a “memory miss”, is rare enough that most memory references will be to addresses represented in the cache. References to addresses in the cache are called “memory hits”; the percentage of memory references found in the cache is called the “hit ratio”.
It is possible, though artificial, to write programs that will not display locality and thus defeat the cache design. Most modern compilers will arrange data structures to take advantage of locality, thus putting the cache system to best use.
Effective Access Time for Multilevel Memory
We have stated that the success of a multilevel memory system is due to the principle of locality. The measure of the effectiveness of this system is the hit ratio, reflected in the effective access time of the memory system.
We shall consider a multilevel memory system with primary and secondary memory. What we derive now is true for both cache memory and virtual memory systems. In this course, we shall use cache memory as an example. This could easily be applied to virtual memory.
In a standard memory system, an addressable item is referenced by its address. In a two level memory system, the primary memory is first checked for the address. If the addressed item is present in the primary memory, we have a hit, otherwise we have a miss. The hit ratio is defined as the number of hits divided by the total number of memory accesses; 0.0 £ h £ 1.0. Given a faster primary memory with an access time TP and a slower secondary memory with access time TS, we compute the effective access time as a function of the hit ratio. The applicable formula is TE = h·TP + (1.0 – h)·TS.
RULE: In this formula we must have TP < TS. This inequality defines the terms “primary”
and “secondary”. In this course TP
always refers to the cache memory.
For our first example, we
consider cache memory, with a fast
cache acting as a front-end for primary memory.
In this scenario, we speak of cache
hits and cache misses. The hit ratio is also called the cache hit ratio in these
circumstances. For example, consider TP
= 10 nanoseconds and TS = 80 nanoseconds. The formula for effective access time becomes
TE = h·10 + (1.0 – h)·80. For sample values of hit ratio
Hit Ratio Access Time
0.5 45.0
0.9 17.0
0.99 10.7
The reason that cache memory works is that the principle of locality enables high values of the hit ratio; in fact h ³ 0.90 is a reasonable value. For this reason, a multi-level memory structure behaves almost as if it were a very large memory with the access time of the smaller and faster memory. Having come up with a technique for speeding up our large monolithic memory, we now investigate techniques that allow us to fabricate such a large main memory.
Cache
Memory Organization
We
now turn our attention to strategies for organizing data in a cache. While this discussion is cast in terms of a
single–level cache, the basic principles apply to every level in a
multi–level cache. In this section, we
use the term “memory”, sometimes “secondary memory”, to refer to the
memory attached to the cache. It is
possible that this memory is either the primary DRAM or a slower and larger
cache
The mapping of the secondary memory to the smaller cache is “many to one” in that each cache block can contain a number of secondary memory addresses. To compensate for each of these, we associate a tag with each cache block, also called a “cache line”.
For example, consider a byte–addressable memory with 24–bit addresses and 16 byte blocks. The memory address would have six hexadecimal digits. Consider the 24–bit address 0xAB7129. The block containing that address contains every item with address beginning with 0xAB712: 0xAB7120, 0xAB7121, … , 0xAB7129, 0xAB712A, … 0xAB712F.
We should point out immediately that the secondary memory will be divided into blocks of size identical to the cache line. If the secondary memory has 16–byte blocks, this is due to the organization of the cache as having cache lines holding 16 bytes of data.
The primary block would have 16 entries, indexed 0 through F. It would have the 20–bit tag 0XAB712 associated with the block, either explicitly or implicitly.
At system start–up, the faster cache contains no valid data, which are copied as needed from the slower secondary memory. Each block would have three fields associated with it
The tag field identifying the memory addresses contained
Valid
bit set to 0 at system start–up.
set to
1 when valid data have been copied into the block
Dirty
bit set to 0 at system start–up.
set to
1 whenever the CPU writes to the faster memory
set to
0 whenever the contents are copied to the slower memory.
The basic unit of a cache is called a “cache line”, which comprises the data copied from the slower secondary memory and the required ID fields. A 16–KB cache might contain 1,024 cache lines with the following structure.
|
D bit |
V Bit |
Tag |
16 indexed entries (16 bytes total) |
|
0 |
1 |
0xAB712 |
M[0xAB7120] … M[0xAB712F] |
We now face a problem that is unique to cache memories. How do we find an addressed item? In the primary memory, the answer is simple; just go to the address and access the item. The cache has much fewer addressable entities than the secondary memory. For example, this cache has 16 kilobytes set aside to store a selection of data from a 16 MB memory. It is not possible to assign a unique address for each possible memory item.
The choice of where in the cache to put a memory block is called the placement problem. The method of finding a block in the cache might be called the location problem. We begin with the simplest placement strategy. When a memory block is copied into a cache line, just place it in the first available cache line. In that case, the memory block can be in any given cache line. We now have to find it when the CPU references a location in that block.
The Associative Cache
The most efficient search strategy is based on associative memory, also called content addressable memory. Unlike sequential searches or binary search on an array, the contents of an associative memory are all searched at the same time. In terminology from the class on algorithm analysis, it takes one step to search an associative memory.
Consider an array of 256 entries, indexed from 0 to 255 (or 0x0 to 0xFF). Suppose that we are searching the memory for entry 0xAB712. Normal memory would be searched using a standard search algorithm, as learned in beginning programming classes. If the memory is unordered, it would take on average 128 searches to find an item. If the memory is ordered, binary search would find it in 8 searches.
Associative memory would find the item in one search. Think of the control circuitry as “broadcasting” the data value (here 0xAB712) to all memory cells at the same time. If one of the memory cells has the value, it raises a Boolean flag and the item is found.
We do not consider duplicate entries in the associative memory. This can be handled by some rather straightforward circuitry, but is not done in associative caches. We now focus on the use of associative memory in a cache design, called an “associative cache”.
Assume a number of cache lines, each holding 16 bytes. Assume a 24–bit address. The simplest arrangement is an associative cache. It is also the hardest to implement.
Divide the 24–bit address into two parts: a 20–bit tag and a 4–bit offset. The 4–bit offset is used to select the position of the data item in the cache line.
|
Bits |
23 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Fields |
Tag |
Offset |
A cache line in this arrangement would have the following format.
|
D bit |
V Bit |
Tag |
16 indexed entries |
|
0 |
1 |
0xAB712 |
M[0xAB7120] … M[0xAB712F] |
The placement of the
16 byte block of memory into the cache would be determined by a cache line replacement policy. The policy would probably be as follows:
1. First, look for a cache line with V = 0. If one is found, then it is “empty”
and available, as
nothing is lost by writing into it.
2. If all cache lines have V = 1, look for one with D = 0. Such a cache line
can be overwritten
without first copying its contents back to main memory.
When the CPU issues an address for memory access, the cache logic determines the part that is to be used for the cache line tag (here 0xAB712) and performs an associative search on the tag part of the cache memory. Only the tag memory in an associative cache is set up as true associative memory; the rest is standard SRAM. One might consider the associative cache as two parallel memories, if that helps.
After one clock cycle, the tag is either found or not found. If found, the byte is retrieved. If not, the byte and all of its block are fetched from the secondary memory.
The Direct Mapped Cache
This strategy is simplest to implement, as the cache line index is determined by the address. Assume 256 cache lines, each holding 16 bytes. Assume a 24–bit address. Recall that 256 = 28, so that we need eight bits to select the cache line.
Divide the 24–bit address into three fields: a 12–bit explicit tag, an 8–bit line number, and a 4–bit offset within the cache line. Note that the 20–bit memory tag is divided between the 12–bit cache tag and 8–bit line number.
|
Bits |
23 – 12 |
11 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Cache View |
Tag |
Line |
Offset |
|
Address View |
Block Number |
Offset |
|
Consider the address
0xAB7129. It would have
Tag = 0xAB7
Line = 0x12
Offset = 0x9
Again, the cache line would contain M[0xAB7120] through M[0xAB712F]. The cache line would also have a V bit and a D bit (Valid and Dirty bits). This simple implementation often works, but it is a bit rigid. Each memory block has one, and only one, cache line into which it might be placed. A design that is a blend of the associative cache and the direct mapped cache might be useful.
An N–way set–associative cache uses direct mapping, but allows a set of N memory blocks to be stored in the line. This allows some of the flexibility of a fully associative cache, without the complexity of a large associative memory for searching the cache.
Suppose a 2–way set–associative implementation of the same cache memory. Again assume 256 cache lines, each holding 16 bytes. Assume a 24–bit address. Recall that 256 = 28, so that we need eight bits to select the cache line. Consider addresses 0xCD4128 and 0xAB7129. Each would be stored in cache line 0x12. Set 0 of this cache line would have one block, and set 1 would have the other.
|
Entry 0 |
Entry 1 |
||||||
|
D |
V |
Tag |
Contents |
D |
V |
Tag |
Contents |
|
1 |
1 |
0xCD4 |
M[0xCD4120] to M[0xCD412F] |
0 |
1 |
0xAB7 |
M[0xAB7120] to M[0xAB712F] |
Examples of Cache Memory
We need to review cache memory and work some specific examples. The idea is simple, but fairly abstract. We must make it clear and obvious. To review, we consider the main memory of a computer. This memory might have a size of 384 MB, 512 MB, 1GB, etc. It is divided into blocks of size 2K bytes, with K > 2.
In
general, the N–bit address is broken into two parts, a block tag and an offset.
The most significant (N
– K) bits of the address are the block tag
The least significant K
bits represent the offset within the block.
We
use a specific example for clarity.
We have a byte
addressable memory, with a 24–bit address.
The cache block size is
16 bytes, so the offset part of the address is K = 4 bits.
In
our example, the address layout for main memory is as follows:
Divide the 24–bit address into two parts: a 20–bit tag and a 4–bit offset.
|
Bits |
23 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Fields |
Tag |
Offset |
Let’s examine the sample address, 0xAB7129, in terms of the bit divisions above.
|
Bits: |
23 – 20 |
19 – 16 |
15 – 12 |
11 – 8 |
7 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Hex Digit |
A |
B |
7 |
1 |
2 |
9 |
|
Field |
0xAB712 |
0x09 |
||||
So, the tag field for this block contains the value 0xAB712. The tag field of the cache line must also contain this value, either explicitly or implicitly. It is the cache line size that determines the size of the blocks in main memory. They must be the same size, here 16 bytes.
All cache memories are divided into a number of cache lines. This number is also a power of two. Our example has 256 cache lines. Where in the cache is the memory block placed?
Associative Cache
As
a memory block can go into any available cache line, the cache tag must
represent
the memory tag explicitly: Cache Tag =
Block Tag. In our example, it is
0xAB712.
Direct Mapped and Set–Associative Cache
For any specific memory block, there is exactly one cache line that can contain it.
Suppose an N–bit address space. 2L cache lines, each of 2K bytes.
|
Address Bits |
(N – L – K) bits |
L bits |
K bits |
|
Cache Address |
Cache Tag |
Cache Line |
Offset |
|
Memory Address |
Memory Block Tag |
Offset |
|
To retrieve the memory block tag from the cache tag, just append the cache line number.
In
our example: The Memory Block Tag = 0xAB712
Cache Tag = 0xAB7
Cache Line = 0x12
Reading From and Writing to the Cache
Let’s begin our review of cache memory by considering the two processes: CPU Reads from Cache and CPU Writes to Cache.
Suppose for the moment that we have a direct mapped cache, with line 0x12 as follows:
|
Tag |
Valid |
Dirty |
Contents (Array of 16 entries) |
|
0xAB7 |
1 |
0 |
M[0xAB7120] to M[0xAB712F] |
Since the cache line has contents, by definition we must have Valid = 1. For this example, we assume that Dirty = 0 (but that is almost irrelevant here).
Read from Cache.
The CPU loads a register from address 0xAB7123. This is read directly from the cache.
Write to Cache
The CPU copies a register into address 0xAB712C. The appropriate page is present in the cache line, so the value is written and the dirty bit is set; Dirty = 1. Note that the dirty bit is not tested, it is just set to 1. All that matters is that there has been at least one write access to this cache line.
Here is a question that cannot occur for reading from the cache. Writing to the cache has changed the value in the cache. The cache line now differs from the corresponding block in main memory. Eventually, the value written to the cache line must be copied back to the secondary memory, or the new value will be lost. The two main solutions to this problem are called “write back” and “write through”.
Write Through
In this strategy, every byte that is written to a cache line is immediately written back to the corresponding memory block. Allowing for the delay in updating main memory, the cache line and cache block are always identical. The advantage is that this is a very simple strategy. No “dirty bit” needed. The disadvantage in the simple implementation is that writes to cache proceed at main memory speed. Many modern primary memories now have a write queue, which is a fast memory containing entries to be written to the slower memory. As long as the queue does not fill, it can accept data at cache speeds.
Write Back
In this strategy, CPU writes to the cache line do not automatically cause updates of the corresponding block in main memory.
The cache line is written back only when it is replaced. The advantage of this is that it is a faster strategy. Writes always proceed at cache speed. Furthermore, this plays on the locality theme. Suppose each entry in the cache is written, a total of 16 cache writes. At the end of this sequence, the cache line will eventually be written to the slower memory. This is one slow memory write for 16 cache writes. The disadvantage of this strategy is that it is more complex, requiring the use of a dirty bit.
Cache Line Replacement
Assume that memory block 0xAB712 is present in cache line 0x12. We now get a memory reference to address 0x895123. This is found in memory block 0x89512, which must be placed in cache line 0x12. The following holds for both a memory read from or memory write to 0x895123. The process is as follows.
1. The
valid bit for cache line 0x12 is examined.
If (Valid = 0), there is nothing
in the cache line, so go to
Step 5.
2. The
memory tag for cache line 0x12 is examined and compared to the desired
tag 0x895. If (Cache Tag = 0x895) go to Step 6.
3. The
cache tag does not hold the required value.
Check the dirty bit.
If (Dirty = 0) go to Step 5.
4. Here, we have (Dirty = 1). Write the cache line back to memory block 0xAB712.
5. Read memory block 0x89512 into cache line 0x12. Set Valid = 1 and Dirty = 0.
6. With the desired block in the cache line, perform the memory operation.
We have three different major strategies for cache mapping.
Direct Mapping is the simplest strategy, but it is rather rigid. One can devise “almost realistic” programs that defeat this mapping. It is possible to have considerable page replacement with a cache that is mostly empty.
Fully Associative offers the most flexibility, in that all cache lines can be used. This is also the most complex, because it uses a larger associative memory, which is complex and costly.
N–Way Set Associative is a mix of the two strategies. It uses a smaller (and simpler) associative memory. Each cache line holds N = 2K sets, each the size of a memory block. Each cache line has N cache tags, one for each set.
Consider variations of mappings to store 256 memory blocks.
Direct Mapped Cache 256 cache lines
“1–Way Set Associative” 256 cache lines 1 set per line
2–Way Set Associative 128 cache lines 2 sets per line
4–Way Set Associative 64 cache lines 4 sets per line
8–Way Set Associative 32 cache lines 8 sets per line
16–Way Set Associative 16 cache lines 16 sets per line
32–Way Set Associative 8 cache lines 32 sets per line
64–Way Set Associative 4 cache lines 64 sets per line
128–Way Set Associative 2 cache lines 128 sets per line
256–Way Set Associative 1 cache line 256 sets per line
Fully Associative Cache 256 sets
N–Way
Set Associative caches can be seen as a hybrid of the Direct Mapped Caches
and Fully Associative Caches. As N goes
up, the performance of an N–Way Set Associative cache improves. After about N = 8, the improvement is so
slight as not to be worth the additional cost.
Cache Memory in Modern Computer Systems
The above discussion of a single level cache attached to main memory is sufficient to illustrate the main ideas behind cache memory. Modern computer systems have gone far beyond this simple design. We now jump into reality.
Almost
all modern computer systems have either a two–level (L1 and L2) or three–level
(L1, L2, and L3) cache system. Those
that do not, such as the CPU for the IBM z/10, have a four–level cache. Furthermore, all modern designs have a “split cache” for the level 1; there is
an I–cache and D–cache (Instruction Cache and Data Cache) at this level. In order to illustrate the advantages of
these designs, we assume the following two–level design, which is based on the
actual structure found in early Pentium designs.
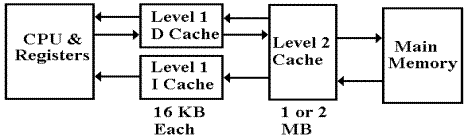
We now address two questions for this design before addressing the utility of a third level in the cache. The first question is why the L1 cache is split into two parts. The second question is why the cache has two levels. Suffice it to say that each design decision has been well validated by empirical studies; we just give a rationale.
There are several reasons to have a split cache, either between the CPU and main memory or between the CPU and a higher level of cache. One advantage is the “one way” nature of the L1 Instruction Cache; the CPU cannot write to it. This means that the I–Cache is simpler and faster than the D–Cache; faster is always better. In addition, having the I–Cache provides some security against self modifying code; it is difficult to change an instruction just fetched and write it back to main memory. There is also slight security against execution of data; nothing read through the D–Cache can be executed as an instruction.
The primary advantage of the split level–1 cache is support of a modern pipelined CPU. A pipeline is more akin to a modern assembly line. Consider an assembly line in an auto plant. There are many cars in various stages of completion on the same line. In the CPU pipeline, there are many instructions (generally 5 to 12) in various stages of execution. Even in the simplest design, it is almost always the case that the CPU will try to fetch an instruction in the same clock cycle as it attempts to read data from memory or write data to memory.
Here is a schematic of the pipelined CPU for the MIPS computer.
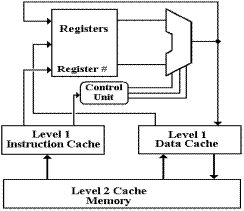 This
shows two of the five stages of the MIPS pipeline. In any one clock period, the control unit
will access the Level 1 I–Cache and the ALU might access the L1 D–Cache. As the I–Cache and
This
shows two of the five stages of the MIPS pipeline. In any one clock period, the control unit
will access the Level 1 I–Cache and the ALU might access the L1 D–Cache. As the I–Cache and
D–Cache are separate memories, they can be accessed at the same time with no
conflict.
We note here that the ALU does not directly access the D–Cache; it is the control unit either feeding data to a register or writing the output from the ALU to primary memory, through the D–Cache. The basic idea is sound: two memory accesses per clock tick.
There is one slight objection possible to the split–cache design. As we noted above, increasing the hit rate on a cache memory results in faster access to the contents of both that cache and, indirectly, the memory being served by that cache. It should be obvious that the cache hit rate is lower for each of the smaller split L1 caches that it would be for a larger combined L1 cache. Empirical data suggests that the advantage of simultaneous access to both instructions and data easily overcomes the disadvantage of the slightly increased miss rate. Practical experience with CPU design validates these empirical data.
The next question relates to the multiplicity of cache levels. Why have a 64–KB L1 cache and a 1–MB (1,024 KB) L2 cache in preference to a 1,092–KB unified cache. Here is an answer based on data for the Apple iMAC G5, as reported in class lectures by David Patterson [R77]. The access times and sizes for the various memory levels are as follows:
|
|
Registers |
L1 I–Cache |
L1 D–Cache |
L2 Cache |
DRAM |
|
Size |
1 KB |
64 KB |
32 KB |
512 KB |
256 MB |
|
Access Time |
0.6 ns |
1.9 ns |
1.9 ns |
6.9 ns |
55 ns |
The basic point is that smaller caches have faster access times. This, coupled with the principle of locality implies that the two–level cache will have better performance than a larger unified cache. Again, industrial practice has born this out.
The
utility of a multi–level cache is illustrated by the following example, based
on the
access times given in the previous table.
Suppose the following numbers for each of the three memory levels.
L1 Cache Access Time = 0.60 nanoseconds Hit rate = 95%
L2 Cache Access Time = 1.90 nanoseconds Hit rate = 98%
Main Memory Access Time = 55.0 nanoseconds.
The one–level cache would be
implemented with the access time and hit rate of the L2
cache, as the one–level cache would be that size. The effective access time is thus:
TE = 0.98·1.90
+ (1 – 0.98)·55.0
= 0.98·1.90
+ 0.02·55.0
= 1.862 + 1.10 = 2.972.
The two–level cache would use
the L1 and L2 caches above and have access time:
TE = 0.95·0.60
+ (1 – 0.95)·[0.98·1.90
+ (1 – 0.98)·55.0]
= 0.95·0.60 + 0.05·2.972
= 0.570 + 0.1486 = 0.719 nanoseconds.
The two–level cache system is about four times faster than the bigger unified cache.
Cache
and Multi–Core Processors
The goal of every CPU design is to increase performance according to some type of relevant benchmark. One way to do this is to increase the clock rate of the CPU. Another way to do this is to add more cache memory on the CPU chip. As transistor densities increase, both options appear to be appealing. There is, however, a problem with each of the options; as each increases, the power density on the chip increases and the chip temperature climbs into a range not compatible with stable operation.
One way to handle this heat problem is to devote more of the chip to cache memory and less to computation. As noted by Stallings [R6], “Memory transistors are smaller and have a power density an order of magnitude lower than logic. … the percentage of the chip area devoted to memory has grown to exceed 50% as the chip transistor density has increased.”
Here is a diagram of a quad–core Intel Core i7 CPU. Each core has its own L1 caches as well as dedicated L2 cache. The four cores share an 8–MB Level 3 cache.
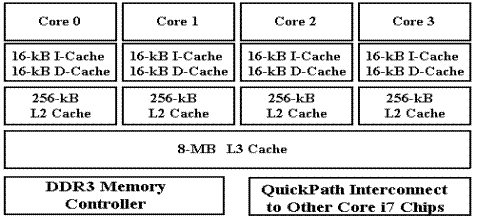
Figure:
Intel Core i7 Block Diagram
Virtual Memory
We now turn to the next example of a memory hierarchy, one in which a magnetic disk normally serves as a “backing store” for primary core memory. This is virtual memory. While many of the details differ, the design strategy for virtual memory has much in common with that of cache memory. In particular, VM is based on the idea of program locality.
Virtual memory has a precise definition and a definition implied by common usage. We discuss both. Precisely speaking, virtual memory is a mechanism for translating logical addresses (as issued by an executing program) into actual physical memory addresses. The address translation circuitry is called a MMU (Memory Management Unit).

This definition alone provides a great advantage to an Operating System, which can then allocate processes to distinct physical memory locations according to some optimization. This has implications for security; individual programs do not have direct access to physical memory. This allows the OS to protect specific areas of memory from unauthorized access.
Virtual Memory in
Practice
Although this is not the definition, virtual memory has always been implemented by pairing a fast DRAM Main Memory with a bigger, slower “backing store”. Originally, this was magnetic drum memory, but it soon became magnetic disk memory. Here again is the generic two–stage memory diagram, this time focusing on virtual memory.
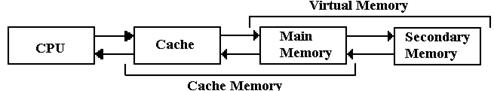
The invention of time–sharing operating systems introduced another variant of VM, now part of the common definition. A program and its data could be “swapped out” to the disk to allow another program to run, and then “swapped in” later to resume.
Virtual memory allows the program to have a logical address space much larger than the computers physical address space. It maps logical addresses onto physical addresses and moves “pages” of memory between disk and main memory to keep the program running.
An address space is the range of addresses, considered as unsigned integers, that can be generated. An N–bit address can access 2N items, with addresses 0 … 2N – 1.
16–bit address 216 items 0 to 65535
20–bit address 220 items 0 to 1,048,575
32–bit address 232 items 0 to 4,294,967,295
In all modern applications, the physical address space is no larger than the logical address space. It is often somewhat smaller than the logical address space. As examples, we use a number of machines with 32–bit logical address spaces.
Machine Physical Memory Logical Address Space
VAX–11/780 16 MB 4 GB (4, 096 MB)
Pentium (2004) 128 MB 4 GB
Desktop Pentium 512 MB 4 GB
Server Pentium 4 GB 4 GB
IBM z/10 Mainframe 384 GB 264
bytes = 234 GB
Organization of
Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is organized very much in the same way as cache memory. In particular, the formula for effective access time for a two–level memory system (pages 381 and 382 of this text) still applies. The dirty bit and valid bit are still used, with the same meaning. The names are different, and the timings are quite different. When we speak of virtual memory, we use the terms “page” and “page frame” rather than “memory block” and “cache line”. In the virtual memory scenario, a page of the address space is copied from the disk and placed into an equally sized page frame in main memory.
Another minor difference between standard cache memory and virtual memory is the way in which the memory blocks are stored. In cache memory, both the tags and the data are stored in a single fast memory called the cache. In virtual memory, each page is stored in main memory in a place selected by the operating system, and the address recorded in a page table for use of the program.
Here is an example based on a configuration that runs through this textbook. Consider a computer with a 32–bit address space. This means that it can generate 32–bit logical addresses. Suppose that the memory is byte addressable, and that there are 224 bytes of physical memory, requiring 24 bits to address. The logical address is divided as follows:
|
Bits |
31 – 28 |
27 – 24 |
23 – 20 |
19 – 16 |
15 – 12 |
11 – 8 |
7 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Field |
Page Number |
Offset in Page |
||||||
The physical address associated with the page frame in main memory is organized as follows
|
Bits |
23 – 20 |
19 – 16 |
15 – 12 |
11 – 8 |
7 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Field |
Address Tag |
Offset in Page Frame |
||||
Virtual memory uses the page
table to translate virtual addresses into physical addresses. In most systems, there is one page table per
process. Conceptually, the page table is
an array, indexed by page frame of the address tags associated with each
process. But note that such an array can
be larger than the main memory itself.
In our example, each address tag is a
12–bit value, requiring two bytes to store, as the architecture cannot access
fractional bytes. The page number is a
20–bit number, from 0 through 1,048,575.
The full page table would require two megabytes of memory to store.
Each process on a computer will be allocated a small page table containing mappings for the most recently used logical addresses. Each table entry contains the following information:
1. The
valid bit, which indicates whether or not there is a valid address tag
(physical
page number) present in that
entry of the page table.
2. The
dirty bit, indicating whether or not the data in the referenced page frame
has been altered by the
CPU. This is important for page
replacement policies.
3. The
20–bit page number from the logical address, indicating what logical page
is being stored in the
referenced page frame.
4. The 12–bit unsigned number representing the address tag (physical page number).
More on Virtual
Memory: Can It Work?
Consider again the virtual memory system just discussed. Each memory reference is based on a logical address, and must access the page table for translation.
But wait! The
page table is in memory.
Does this imply
two memory accesses for each memory reference?
This is where the TLB (Translation Look–aside Buffer) comes in. It is a cache for a page table, more accurately called the “Translation Cache”.
The TLB is usually implemented
as a split associative cache.
One associative cache for
instruction pages, and
One associative cache for data
pages.
A page table entry in main memory is accessed only if the TLB has a miss.
The Complete Page
Table Structure
All page tables are under the control of the Operating System, which creates a page table for each process that is loaded into memory. The computer hardware will provide a single register, possibly called PTA (Page Table Address) that contains the address of the page table for each process, along with other information.
Each page table,
both the master table and each process table, has contents that vary depending
on the value in the valid bit.
If Valid = 1, the contents are the
12–bit address tag.
If Valid = 0, the contents are the
disk address of the page as stored on disk.
As the above
implies, the page table for a given process may be itself virtualized; that is
mostly stored in virtual memory. Only a
small part of a processes full page table must be in physical memory for fast
access. Of that, a smaller part is in
the TLB for faster access.
Virtual Memory with Cache Memory
Any modern computer supports both virtual memory and cache memory. We now consider the interaction between the two.
The following example will illustrate the interactions. Consider a computer with a 32–bit address space. This means that it can generate 32–bit logical addresses. Suppose that the memory is byte addressable, and that there are 224 bytes of physical memory, requiring 24 bits to address. The logical address is divided as follows:
|
Bits |
31 – 28 |
27 – 24 |
23 – 20 |
19 – 16 |
15 – 12 |
11 – 8 |
7 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Field |
Page Number |
Offset in Page |
||||||
We suppose further that virtual memory implemented using page sizes of 212 = 4096 bytes, and that cache memory implemented using a fully associative cache with cache line size of 16 bytes. The physical address is divided as follows:
|
Bits |
23 – 20 |
19 – 16 |
15 – 12 |
11 – 8 |
7 – 4 |
3 – 0 |
|
Field |
Memory Tag |
Offset |
||||
Consider a memory access, using the virtual memory. Conceptually, this is a two–step process. First, the logical address is mapped into a physical address using the virtual memory system. Then the physical address is sent to the cache system to determine whether or not there is a cache hit.
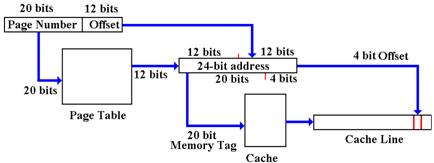
Figure: Two–Stage Virtual Address
Translation
The Virtually Mapped
Cache
One solution to the inefficiencies of the above process is to use a virtually mapped cache. In our example we would use the high order 28 bits as a virtual tag. If the addressed item is in the cache, it is found immediately.
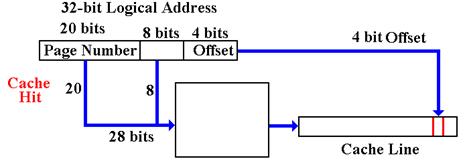
A Cache Miss accesses the Virtual Memory system.
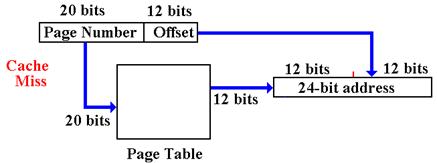
The Problem of Memory
Aliasing
While the virtually mapped cache presents many advantages, it does have one notable drawback when used in a multiprogramming environment. In such an environment, a computer might be simultaneously executing more than one program. In the real sense, only one program at a time is allocated to any CPU. Thus, we might have what used to be called “time sharing”, in which a CPU executes a number of programs in sequence.
There is a provision in such a system for two or more cooperating processes to request use of the same physical memory space as a mechanism for communication. If two or more processes have access to the same physical page frame, this is called memory aliasing. In such scenarios, simple VM management systems will fail. This problem can be handled, as long as one is aware of it.
The topic of virtual memory is worthy of considerable study. Mostly it is found in a course on Operating Systems. The reader is encouraged to consult any one of the large number of excellent textbooks on the subject for a more thorough examination of virtual memory.
Solved Problems
Here are some solved problems related to byte ordering in memory.
1. Suppose one has the following memory map as a
result of a core dump.
The memory is byte addressable.
|
Address |
0x200 |
0x201 |
0x202 |
0x203 |
|
Contents |
02 |
04 |
06 |
08 |
What is the value of the 32–bit long integer stored at address 0x200?
This is stored in the four bytes at addresses 0x200, 0x201, 0x202, and 0x203.
Big Endian: The number is 0x02040608, or 0204
0608. Its decimal value is
2·2563 + 4·2562 + 6·2561
+ 8·1
= 33,818,120
Little Endian: The number is 0x08060402, or 0806 0402. Its decimal value is
8·2563
+ 6·2562
+ 4·2561
+ 2·1
= 134,611,970.
NOTE: Read the bytes backwards, not the hexadecimal
digits.
Powers of 256 are 2560 = 1, 2561 = 256,
2562
= 65536, 2563 = 16,777,216
2. Suppose
one has the following memory map as a result of a core dump.
The memory is byte addressable.
|
Address |
0x200 |
0x201 |
0x202 |
0x203 |
|
Contents |
02 |
04 |
06 |
08 |
What is the value of the 16–bit integer stored at address 0x200?
This is stored in the two bytes at addresses 0x200 and 0x201.
Big Endian The value is 0x0204.
The decimal value
is 2·256
+ 4 = 516
Little Endian: The value is 0x0402.
The decimal value
s 4·256
+ 2 = 1,026
Note: The bytes at addresses 0x202 and 0x203 are not part of this 16–bit integer.
3. You are asked to implement a 128M by 32
memory (1M = 220), using only
16M by 8 memory chips.
a) What
is the minimum size of the MAR?
b) What
is the size of the MBR?
c) How
many 16M by 8 chips are required for this design?
Answer: a) 128M = 27·220 = 227, so the minimum MAR size is 27 bits.
b) The MBR size
is 32 bits.
c) 128M·32 / 16M·8
= 8·4 = 32 chips.
4. Complete the following table describing the memory and chip count needed to fabricate.
|
Memory System Capacity |
Number of bits in MAR |
Number of bits in MBR |
Number of Chips Needed if the capacity of each chip is |
||
|
|
|
|
1K by 4 |
2K by 1 |
1K by 8 |
|
64K by 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64K by 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
32K by 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
32K by 16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
32K by 32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10K by 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10K by 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
ANSWER: We begin by
showing the general formulae and then giving a few specific answers. First, we must define some variables, so that
we may state some equations.
Let N1 be the number of addressable units in the
memory system
M1 be the number of bits for each entry in the memory system
N2 be the number of addressable units in the memory chip
M2 be the number of bits for each entry in the memory chip.
So
that for making a 64K by 4 memory from a 1K by 8 chip, we have
N1 = 64K = 26·210 = 216, as 1K = 210 =
1,024.
M1 = 4
N2 = 1K = 210.
M2 = 8.
Number of bits in MAR and MBR
These
numbers are defined by the memory system parameters and have nothing to do with
the memory chips used to construct the memory.
For a N1 by M1 memory system, we have
P bits in the MAR, where 2P–1
< N1 £ 2P.
M1 bits in the MBR.
Note
that in most modern computers, the actual number of bits in the MAR is set at
design time and does not reflect the actual memory size. Thus, all computers in the Pentium™ class
have 32-bit MAR’s, even if the memory is 256MB = 256·1MB = 28·220B = 228 bytes.
N1 = 32K = 25·210 = 215. Solve 2P–1 < 215 £ 2P to get P = 15, or 15 bits in the MAR.
N1 = 64K = 26·210 = 216. Solve 2P–1 < 216 £ 2P to get P = 16, or 16 bits in the MAR.
N1 = 10K = 5·2K = 5·211
= 1.25·213, not a power
of 2.
Solve 2P–1 < 1.25·213 £ 2P to get P = 14. Note that 213 = 8K and 214
= 16K.
With
this much, we may start filling in the table.
|
Memory System Capacity |
Number of bits in MAR |
Number of bits in MBR |
Number of Chips Needed if the capacity of each chip is |
||
|
|
|
|
1K by 4 |
2K by 1 |
1K by 8 |
|
64K by 4 |
16 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
64K by 8 |
16 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
32K by 4 |
15 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
32K by 16 |
15 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
32K by 32 |
15 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
10K by 8 |
14 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
10K by 10 |
14 |
10 |
|
|
|
For
most of the table, one may compute the number of chips needed by the following
formula: Chips = (N1 ·
M1) / (N2 · M2), or the total number of
bits in the memory system divided by the total number of bits in the memory
chip. In actual fact, this works only
when one of the two following conditions holds:
either M1 / M2 is a whole
number (as M1 = 4 and M2 = 1),
or M2 / M1 is a whole number
(as M1 = 4 and M2 = 8).
The
analysis in the 10K-by-10 case, in which neither of these conditions holds, is
a bit more complicated. Here we present
a detailed discussion of the 64K-by-4 case, followed by the answers to all but
the 10K-by-10 case, which we also discuss in detail.
For
64K-by-4 fabricated from 1K-by-4, it is obvious that each 4-bit entry in the
memory system is stored in one 4-bit memory chip, so that the total number of
chips required is simply 64, or (64K · 4) / (1K · 4).
For
64K-by-4 fabricated from 2K-by-1 chips, it should be obvious that four entries
in the
2K-by-1 chip are required to store each of the 4-bit entries in the memory
system. The easiest way to achieve this
goal is to arrange the memory chips in “banks”, with four of the chips to each
bank. The number of banks required is
64K / 2K = 32, for a total of 128 chips.
Note that this agrees with the result (64K · 4) / (2K · 1) = 256K / 2K = 128.
For
64K-by-4 fabricated from 1K-by-8 chips, it should be obvious that the 8-bit
entries in the chip can store two of the 4-bit entries in the memory
system. For this reason, each 1K-by-8
chip can store 2K entries in the main memory and the number of chips needed is
64K / 2K or 32. This answer is the same
as (64K · 4) / (1K · 8) = 256K / 8K = 32.
From
this point until the 10K-by-8 entry we may just argue relative sizes of the
memories, so that the 64K-by-8 memory is twice the size of the 64K-by-4, the
32K-by-4 memory is half the size of the 64K-by-4 memory, etc.
We
now present the table to this point.
|
Memory System Capacity |
Number of bits in MAR |
Number of bits in MBR |
Number of Chips Needed if the capacity of each chip is |
||
|
|
|
|
1K by 4 |
2K by 1 |
1K by 8 |
|
64K by 4 |
16 |
4 |
64 |
128 |
32 |
|
64K by 8 |
16 |
8 |
128 |
256 |
64 |
|
32K by 4 |
15 |
4 |
32 |
64 |
16 |
|
32K by 16 |
15 |
16 |
128 |
256 |
64 |
|
32K by 32 |
15 |
32 |
256 |
512 |
128 |
|
10K by 8 |
14 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
10K by 10 |
14 |
10 |
|
|
|
10K-by-8 memory
From 1K-by-4
(N1 · M1) / (N2 · M2) = (10K · 8) / (1K · 4) = 80K / 4K = 20
From 2K-by-1
(N1 · M1) / (N2 · M2) = (10K · 8) / (2K · 1) = 80K / 2K = 40
From 1K-by-8
(N1 · M1) / (N2 · M2) = (10K · 8) / (1K · 8) = 80K / 8K = 10
10K-by-10 memory
From 2K-by-1
(N1 · M1) / (N2 · M2) = (10K · 10) / (2K · 1) = 100K / 2K = 50
We run into trouble with the 1K-by-4
chips because 10/4 = 2.5; thus 4 does not divide 10.
The problem is how to spread two
entries (20 bits) over five chips and retrieve the 10-bit
words efficiently. It cannot be done; one must allocate three
chip entries per 10-bit word.
From 1K-by-4
We solve (N1 / N2) · éM1
/ M2ù = (10K / 1K) · é10
/ 4ù = 10 · 3 = 30.
From 1K-by-4
We solve (N1 / N2) · éM1
/ M2ù = (10K / 1K) · é10
/ 8ù = 10 · 2 = 20.
|
Memory System Capacity |
Number of bits in MAR |
Number of bits in MBR |
Number of Chips Needed if the capacity of each chip is |
||
|
|
|
|
1K by 4 |
2K by 1 |
1K by 8 |
|
64K by 4 |
16 |
4 |
64 |
128 |
32 |
|
64K by 8 |
16 |
8 |
128 |
256 |
64 |
|
32K by 4 |
15 |
4 |
32 |
64 |
16 |
|
32K by 16 |
15 |
16 |
128 |
256 |
64 |
|
32K by 32 |
15 |
32 |
256 |
512 |
128 |
|
10K by 8 |
14 |
8 |
20 |
40 |
10 |
|
10K by 10 |
14 |
10 |
30 |
50 |
20 |
5. A 256-word memory has its words numbered from 0 to 255. Define the address bits for
each of the following. Each address bit should be specified as 0, 1,
or d (don’t-care).
a) Word 48
b) Lower
half of memory (words 0 through 127)
c) Upper
hald of memory (words 128 through 255)
d) Even
memory words (0, 2, 4, etc.)
e) Any
of the eight words 48 through 55.
ANSWER:
Note that 28 = 256, so we need an 8-bit address for this memory.
Recall
that memory addresses are unsigned integers, so that we are dealing with
unsigned
eight-bit integers here. The bit values
are given in this table.
|
Bit |
B7 |
B6 |
B5 |
B4 |
B3 |
B2 |
B1 |
B0 |
|
Value |
128 |
64 |
32 |
16 |
8 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
So,
in eight-bit unsigned binary we have decimal 128 = 1000 0000 in binary, and
decimal
127 = 128 – 1 = 0111 1111 in binary.
a) Word
48.
The answer here is just the
binary representation of decimal 48.
Since 48 = 32 + 16, the
answer is 0011 0000.
NOTE: This is an eight-bit number, so it
needs two leading 0’s.
b) Words
0 through 127.
We represent each address and
then determine what bits are common.
Decimal 0 = 0000 0000, and
Decimal 127 = 0111 1111, so the answer is 0ddd dddd.
Any address beginning with a
0 is in the lower half of memory.
c) Words
128 through 255.
Decimal 128 = 1000 0000 (unsigned 8-bit binary), and
Decimal 255 = 1111 1111, so the answer is 1ddd dddd.
d) Even
memory words.
Each even number has its
least significant bit equal 0, as the LSB is
the “1 bit”. So the answer is dddd ddd0.
e) Any
of the eight words 48 through 55.
Decimal 48 = 0011 0000 (see
answer a), and
Decimal 55 = 0011 0111 as
55 = 48 + 7,
We look for the common bits
and determine the answer as 0011 0ddd.
6 Design a 16K-by-8 memory using 2K-by-4 memory chips. Arrange the chips in
an 8 by 2 array (8 rows of 2
columns) and design the decoding circuitry.
ANSWER: The first part of the solution is to define
what we are given and what we are asked to build. From that, we can develop the solution,
introducing a new term.
We
are given a collection of 2K-by-4 memory chips.
As 2K = 211, each of these chips has eleven address lines,
denoted A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0,
four data lines, D3D2D1D0, and the
required control and select lines. We
are asked to design a 16K-by-8 memory.
As 16K = 214, this memory has 14 address lines, denoted A13
through A0. The memory to be
designed has eight data lines, denoted D7 through D0, and
necessary control lines.
Because
we are using 4-bit chips to create an 8-bit memory, we shall arrange the chips
in rows of two, with one chip holding the high-order four bits and the other
the low-order four bits of the eight-bit entry.
Each such row is called a bank
of memory. The end result of this design
is the arrangement of memory into a number of rows and two columns. The figure below shows the use of the
columns. The drawing on the left shows
four data lines from each chip feeding four bits in the eight-bit MBR. The drawing at the right shows a common
short-hand for expressing the same drawing.
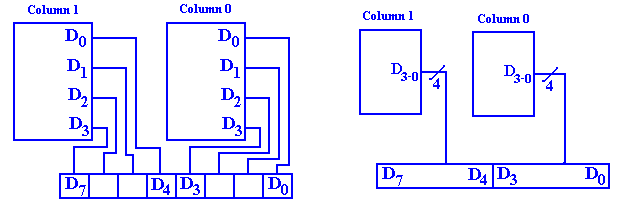
The
design suggested above divides the memory into banks of 2K-by-8, so that we
need
16K / 2K = 8 banks for the memory to be designed. This suggests that we need 8 banks of 2 chips
each for a total of 16 chips. Using the
analysis of problem 3.1, we establish the number of chips needed as (16K · 8) / (2K · 4) = 128K / 8K = 16, as expected.
If
we have 8 banks, each bank containing 2K addresses, we need 3 bits (8 = 23)
to select the bank and 11 bits (2K = 211) to address each chip in
the bank. We have stipulated that the
16K memory requires 14 address lines, as 16K = 214, so we have
exactly the right bit count. There are
two standard ways to split the 14-bit address into a bank select and chip
address.
![]()
Banked
Memory Interleaved
Memory
The observant student will note that the number of ways
to split the 14-bit address into a
3-bit bank number and an 11-bit chip address is exactly
![]()
but that only the two methods mentioned above make any
sense.
The solution presented in these notes will be based on
the interleaved memory model. The basis of the design will be a set of
memory banks, each bank arranged as follows.
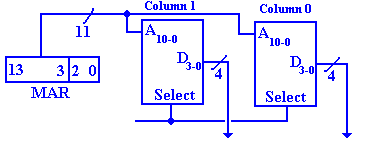
Note that the eleven high-order bits of the system MAR
are sent to each chip in every memory bank.
Note that in each memory bank, both chips are selected at the same
time. We now use a 3-to-8 decoder to
select the memory bank to be accessed.
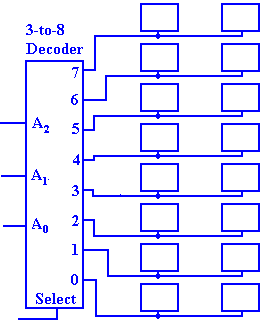
The circuit at left shows the basic layout for the chip
select part of the addressing. This
diagram assumes interleaved memory, in which address bits A2A1A0
serve to select the memory bank that holds the addressed byte and address bits
A13A12A11A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3
are passed as an 11-bit address to each of the sixteen chips.
Again, it would be equally valid to have address bits A13A12A11
as input to the decoder and the low-order 11 bits passed to each chip. This second arrangement is not interleaved
memory.
We now have all of the components of a complete design,
so now let’s show the whole thing.
Here is the complete design of the 16K-by-8 memory as
fabricated from 2K-by-4 chips.
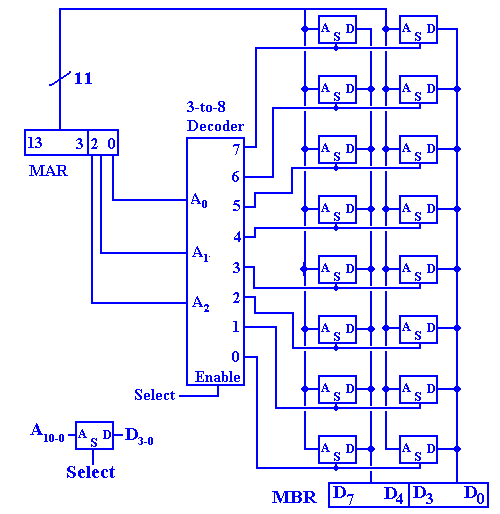
The chip in the lower left explains the notation used in
the main drawing.
For each of the sixteen memory chips, we have the
following
A the eleven address inputs A11-0.
D the four data I/O lines D3D2D1D0.
S the chip select – active high.
7 You are given a 16K-by-4 ROM unit. Convert it to a 64K-by-1 ROM. Treat the
16K-by-4 ROM as one unit that you
cannot alter. Only logic external to
this
16K-by-4 ROM unit is to be used or
shown.
ANSWER: This problem is almost opposite the previous
problem. We are given a ROM (Read-Only
Memory) that is 16K-by-4. As 16K = 214,
the address register for this chip must have 14 bits: A13-0. The data buffer of this memory has four bits:
D3D2D1D0.
The
problem calls for the design of a 64K-by-1 ROM.
As 64K = 216, this memory has a
16-bit address for each bit. Of the
16-bit address that goes to this memory, 14 bits must go to the 16K-by-4 memory
chip and 2 bits used to select one of the four bits output from the chip.
The
only other task is to use a 4-to-1 multiplexer to select which of the 4 bits
from the
16K-by-4 chip is to be used.
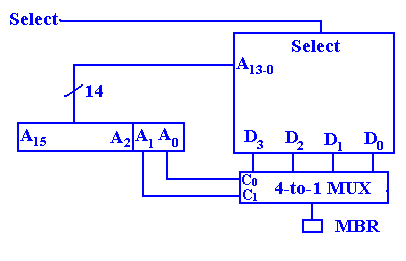
8 A given computer design calls for an 18-bit
MAR and an 8-bit MBR.
a) How many addressable memory
elements can the memory contain?
b) How many bits does each
addressable unit contain?
c) What is the size of the address
space in bytes?
NOTE: The answer can be given in many
ways. If the answer were 16K, you
might say either 16K, 214,
or 16384.
ANSWER: Recall that 218
= 28·210
= 256K = 256·1024 = 262,144.
a) As
the MAR contains 18 bits, the maximum number of addressable units is
218 or 256K. The answer
262,144 is correct, but not favored.
b) As the MBR contains 8 bits, so does each
addressable unit.
The addressable unit is an
8-bit byte.
c) As
a result of the above two answers, the address space is 256KB or 218
bytes.
9 You are asked to design a 128K-by-16 memory
using available chips.
How many 16K-by-4 memory chips would
be required for the design?
ANSWER: (128K
· 16) / (16K · 4) = 2048K / 64K = 32
Equivalently (128K / 16K) · (16 / 4 = 8 · 4 = 32
10 You are given a number of chips and asked to
design a 64KB memory.
You immediately realize that this requires 16 address lines, as 64K = 216. The memory is interleaved, with 12 address
bits (A15 – A4) going to each byte-addressable memory
chip and 4 address bits (A3A2A1A0)
going to select the memory chip.
a) What is the size of each
chip in bytes (or KB)?
b) How many chips are found
in this design?
ANSWER: The memory
chip is byte-addressable, implying that each byte in the chip has a distinct
address and that the number of addresses in the chip equals the number of
bytes.
a) There
are 12 address bits for each of the memory chips,
so each memory chip has 212 bytes =
22·210 bytes = 4·210 bytes = 4KB.
b) There are 4 address lines used to select the
memory chips,
so there must be 24
= 16 chips.
NOTE: The key idea for this and the previous question is
that P bits will select 2P different items, alternately that a P-bit
unsigned binary number can represent decimal numbers in the range 0 to 2P
– 1 inclusive, often written as the closed interval [0, 2P – 1]. As an example, an
8-bit binary number will represent unsigned decimal numbers in the range 0 to 28
– 1, or
0 to 255, while a 16-bit binary number will represent
unsigned decimal numbers in the range
[0, 216 – 1] or [0, 65535].
Another way of saying the same thing is that the
representation of a positive integer N requires P bits where 2P–1
< N £ 2P. This simple idea is important in many areas
of computer science, but seems to elude some students.
11 You are asked to implement a 128M by 32 memory (1M = 220),
using only 16M by 8 memory chips.
a) What
is the minimum size of the MAR?
b) What
is the size of the MBR?
c) How
many 16M by 8 chips are required for this design?
ANSWER: Remember that 128M =27 · 220 = 227 and that 16M = 224.
a) To
address 128M = 227 entries, we need a 27-bit MAR.
b) Since
each entry is 32-bits, we have a 32-bit
MBR.
c) The
number of chips is (128M ·
32) / (16M · 8), which evaluates to
(227 · 25) / (224 · 23) = 232 /227 = 25
= 32.
12 A CPU outputs two control signals: Select and ![]() , interpreted as follows.
, interpreted as follows.
If Select = 0, the memory does
nothing.
If Select = 1, the memory is read if
![]() = 1, otherwise
it is written.
= 1, otherwise
it is written.
Draw a circuit to convert these
two signals into the following control signals
READ If
READ = 1, the CPU reads from memory.
WRITE If WRITE = 1, the CPU writes to memory.
Insure that READ = 1 and WRITE = 1
cannot occur at the same time.
ANSWER: Note, if
Select = 0, then both READ = 0 and WRITE = 0.
if Select =
1 and ![]() = 1, then READ
= 1 and WRITE = 0
= 1, then READ
= 1 and WRITE = 0
if
Select = 1 and ![]() = 0, then READ
= 0 and WRITE = 1.
= 0, then READ
= 0 and WRITE = 1.
The circuit
follows from those observations.
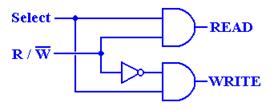
13 A computer has a 24-bit MAR.
Each 16-bit word is individually addressable.
All answers larger than 128 should
be given as a power of two.
a) How
many words can this computer address?
b) Assuming
8-bit bytes, how many bytes can this computer address?
c) What
is the size of the MBR? This is not a
trick question.
ANSWERS: a) The
MAR size is 24 bits; the computer can address 224 words.
This is also 24·220 words = 16·220 words = 16 M words.
b) One 16-bit word = 2 bytes, so the memory size
is 2·224 bytes or 225 bytes.
This is
also 25·220
bytes = 32·220 bytes = 32 M
bytes.
c) The MBR is 16 bits in size, the same as the
size of the addressable unit.
14 Examine the following memory map of a
byte–addressable memory.
Let W refer to address 109.
|
107 |
108 |
109 |
10A |
10B |
|
00 |
11 |
23 |
17 |
CA |
a) Assuming big–endian organization, what is the value of the 16–bit integer at W?
b) Assuming little–endian organization, what is the value of the 16–bit integer at W?
Answer: The 16–bit entry at
address 109 occupies bytes 109 and 10A, as follows.
|
107 |
108 |
109 |
10A |
10B |
|
00 |
11 |
23 |
17 |
CA |
a) In
big–endian, the “big end” is stored first: 2317
b) In little–endian, the “little end” is
stored first 1723.
15 A computer has a cache memory set–up, with the
cache memory having an access time of 6 nanoseconds and the main memory having
an access time of 80 nanoseconds. This
question focuses on the effective access time of the cache.
a) What
is the minimum effective access time for this cache memory?
b) If
the effective access time of this memory is 13.4 nanoseconds, what is the hit
ratio?
ANSWER:
a) The
cache memory cannot have an access time less than that of the cache, so 6 nsec.
b) The
equation of interest here is TE = h·TP + (1 – h)·TS. Using
the numbers, we have
13.4 = h·6 + (1 – h)·80, or 13.4 = 80 – 74·h, or 74·h
= 66.6, or h = 0.9.
16. (20 points)
Suppose a computer using direct mapped cache has 232 words of
main memory and a cache of 1024 blocks, where each cache block contains 32
words.
a) How many blocks of main memory are
there?
b) What is the format of a memory
address as seen by the cache, that is, what are the
sizes of the tag, block, and word
fields?
c) To which cache block will the memory reference
0000 63FA map?
ANSWER: Recall that 1024 = 210 and 32 = 25,
from which we may conclude 1024 = 32 · 32.
a) The number of blocks is 232
/ 25 = 2(32 – 5) = 227
= 27 ·
220 = 128 M = 134, 217, 728.
b) 32 words per cache line Þ Offset address is 5
bits.
1024 blocks in the cache Þ Block number is 10
bits.
232 words Þ 32 bit address Þ 32 – (5 + 10) = 10 – 15 = 17 bit tag.
|
Bits |
31 |
|
15 |
14 |
|
5 |
4 |
|
0 |
|
Contents |
Tag |
Block Number |
Offset within block |
||||||
c) The number of bits allocated to the block
number and offset are 15. We examine
the last four hex digits of 0000
63FA, as they correspond to 16 binary bits.
|
|
15 |
14 |
13 |
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
Hex |
6 |
3 |
F |
A |
||||||||||||
|
Binary |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
|
|
11
0001 1111 = 0x31F |
1
1010 = 0x1A = 26 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0x31F = 3·256 + 1·16
+ 15 = 768 + 16 + 15 = 799.
17 A given computer design calls for an 18-bit MAR and an 8-bit MBR.
a) How many addressable
memory elements can the memory contain?
b) How many bits does each
addressable unit contain?
c) What is the size of the
address space in bytes?
ANSWER: Recall that 218
= 28·210
= 256K = 256·1024 = 262,144.
a) As
the MAR contains 18 bits, the maximum number of addressable units is
218 or 256K. The answer
262,144 is correct, but not favored.
b) As the MBR contains 8 bits, so does each
addressable unit.
The addressable unit is an
8-bit byte.
c) As
a result of the above two answers, the address space is 256KB or 218
bytes.
18 A computer memory system uses a primary memory with 100 nanosecond
access time,
fronted by a cache memory with 8
nanosecond access time. What is the
effective access
time if a) The hit ratio is
0.7?
b) The hit ratio is 0.9?
c) The hit ratio is 0.95?
d) The hit ratio is 0.99?
ANSWER: There is a problem with names here. For the cache scenario, we have
TP as the access time of
the cache
TS as the access time of
the primary memory.
The
equation is TE = h·8
+ (1 – h)·100.
a) h = 0.7 TE
= 0.7·8 + (1 – 0.7)·100 = 0.7·8
+ 0.3·100 = 5.6 + 30.0 = 35.6
b) h = 0.9 TE
= 0.9·8 + (1 – 0.9)·100 = 0.9·8
+ 0.1·100 = 7.2 + 10.0 = 17.2
c) h = 0.95 TE
= 0.95·8 + (1 – 0.95)·100 = 0.95·8
+ 0.05·100 = 7.6 + .5.0 = 12.6
d) h = 0.99 TE
= 0.99·8 + (1 – 0.99)·100 = 0.99·8
+ 0.01·100 = 7.92 + 1.0 = 8.92
19 (20 points) You
are given a 16K x 4 ROM unit. Convert it
to a 32K x 2 ROM.
Use only AND, OR, and NOT gates and
possible D flip–flops in your design.
Treat the 16K x 4 ROM as one unit
you cannot alter. Include only logic
gates external to the ROM unit.
ANSWER:
The 16K by 4 ROM has 16K = 214 addressable
entries, each of 4 bits. We are to
convert this to a 32K by 2 ROM, with 32K = 215 addressable entries,
each of 2 bits. The 15–bit address for
the latter must be broken into a 14–bit address for the former and a selector.
20 The
16–bit number, represented in hexadecimal as 0xCAFE,
is to be stored
at the address 0x40D in a byte–addressable memory.
a)
What are the addresses of the two bytes associated with this 16–bit
number?
b)
What are the contents of these addresses if the number is stored in
big–endian form?
c)
What are the contents of these addresses if the number is stored in
little–endian form?
ANSWER: a) The
number is stored in addresses 0x40D and 0x40E.
b) In big–endian, the more significant byte
is stored first.
0x40D 0xCA
0x40E 0xFE
c) In little–endian, the less significant
byte is stored first.
0x40D 0xFE
0x40E 0xCA
21 Suppose a computer using fully associative cache has 220
words of main memory and a cache of 512 blocks, where each cache block contains
32 bytes.
The memory is byte addressable; each byte has a distinct address.
a) How many blocks of main memory are there?
b) What is the format of a memory
address as seen by the cache, that is, what are the
sizes of the tag and word fields?
Answer: Recall that 32 = 25.
a) The number of blocks is 220
/ 25 = 2(20 – 5) = 215 = 25 · 210 = 32 K = 32,768
b) For associative mapping the address has only
tag and word offset in the block.
32 byte block Þ
5 bit offset.
20 bit address Þ (20 – 5) = 15 bit tag.
|
Bits |
19 |
|
5 |
4 |
|
0 |
|
Contents |
Tag |
Offset in block |
||||
22 A SDRAM memory unit is connected to a CPU via a 500 MHz memory bus.
If the memory bus is 128 bits wide
and the SDRAM is operated at Double Data Rate
(it is a DDR–SDRAM), what is the
maximum burst transfer rate in bytes per second?
ANSWER: The bus is 128 bits
(16 bytes) wide, so it delivers 16 bytes at a time.
It is DDR so it
transfers 32 bytes per clock pulse.
It is DDR at 500 MHz,
so it delivers 500·106
collections of bytes per second.
The data rate is 32·500·106
bytes per second or 16,000·106
bytes per second.
This is 16·109 bytes per second, which is about 14.9 GB/sec.
Note: I shall accept 16.0 GB/sec, though it is technically
incorrect.
23 You are given a D flip–flop, such as shown in
the left diagram. You are to
design a memory cell as shown in the
right diagram. The memory cell I/O line
must be
connected directly to the bus line,
and not pass through any other gates.
The memory cell is controlled by two
inputs: Select and R/![]() .
.
If Select = 0, the cell is
inactive. If Select = 1, it is either
being read or written to.
If R/![]() = 0, the cell
is being written to, and changes state according to its D input.
= 0, the cell
is being written to, and changes state according to its D input.
If R/![]() = 1, the output
of the cell (Q) is being placed on the bus line.
= 1, the output
of the cell (Q) is being placed on the bus line. ![]() is not used.
is not used.
Design
the circuit using only gates that will be internal to the Memory Cell. Recall that the
D flip–flop control signal called “clock” is just a pulse that causes the
flip–flop to change states.
ANSWER: Here we note that the control signals to the cell are as
follows:
The cell is being
written to if and only if Select = 1 and R/![]() = 0.
= 0.
The cell is being read if and only
if Select = 1 and R/![]() = 1.
= 1.
The cell receives
data only when its clock input goes high.
Remember that this is an input
to the flip–flop that activates it
and enables it to receive data. The name
is standard, but a
bit misleading. While this might be connected to the system
clock, it need not be.
Here is the circuit.
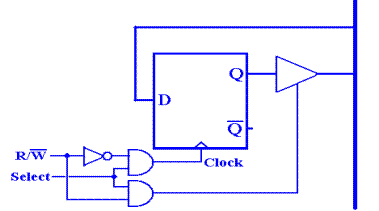
24 A computer has a 24–bit MAR. Each 16–bit word is individually addressable.
All answers larger than 128 should
be given as a power of two.
a) How
many words can this computer address?
b) Assuming
8–bit bytes, how many bytes can this computer address?
c) What
is the size of the MBR?
d) If
this memory is implemented with 2MB (221 by 8) chips, how many
of these chips will be needed?
e) This
memory is set up as low–order
interleaved. Identify the address
lines
that go to each chip and the
address lines used to select the memory bank.
ANSWERS: a) The MAR size is 24 bits; the computer can
address 224 words.
This is also 24·220 words = 16·220 words = 16
M words.
This has a
24–bit address: A23 – A0.
b) One 16-bit word = 2 bytes, so the memory size
is 2·224 bytes or 225 bytes.
This is
also 25·220
bytes = 32·220 bytes = 32 M bytes.
c) The MBR is 16 bits in size, the same as the size of the addressable unit.
d) The chip count is given by dividing the
memory size by the chip size.
As the chips
are sized in bytes, we use this as a common measure.
N = 225
bytes/ 221 bytes = 24 = 16.
e) The memory chips are 2MB. We need memory banks of size 2 megawords,
with the word
size being 16 bits = 2 bytes. Each bank
of memory will have
two of the
chips, one for bits 15 – 8 and the other for bits 7 – 0.
There
will be eight banks of memory, each holding two memory chips.
This accounts
for the 16 chips.
Three
bits will select the bank: A2
– A0.
The high–order
twenty one bits (A23 – A3)
are sent to each bank, and
hence to each
chip in the bank.
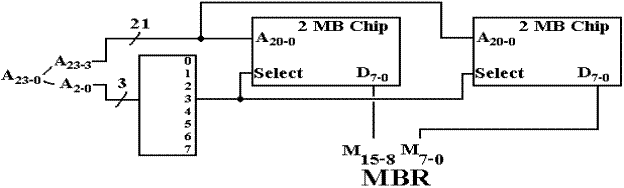
Gulliver’s Travels
and “Big-Endian” vs. “Little-Endian”
The author of these notes has been told repeatedly of the literary antecedents of the terms “big-endian” and “little-endian” as applied to byte ordering in computers. In a fit of scholarship, he decided to find the original quote. Here it is, taken from Chapter IV of Part I (A Voyage to Lilliput) of Gulliver’s Travels by Jonathan Swift, published October 28, 1726.
The edition consulted for these notes was published in 1958 by Random House, Inc. as a part of its “Modern Library Books” collection. The LC Catalog Number is 58-6364.
The story of “big-endian” vs. “little-endian” is described in the form on a conversation between Gulliver and a Lilliputian named Reldresal, the Principal Secretary of Private Affairs to the Emperor of Lilliput. Reldresal is presenting a history of a number of struggles in Lilliput, when he moves from one difficulty to another. The following quote preserves the unusual capitalization and punctuation found in the source material.
“Now, in the midst of these intestine Disquiets, we are threatened with an Invasion from the Island of Blefuscu, which is the other great Empire of the Universe, almost as large and powerful as this of his majesty. ….
[The two great Empires of Lilliput and Blefuscu] have, as I was going to tell you, been engaged in a most obstinate War for six and thirty Moons past. It began upon the following Occasion. It is allowed on all Hands, that the primitive Way of breaking Eggs before we eat them, was upon the larger End: But his present Majesty’s Grand-father, while he was a Boy, going to eat an Egg, and breaking it according to the ancient Practice, happened to cut one of his Fingers. Whereupon the Emperor his Father, published an Edict, commanding all his Subjects, upon great Penalties, to break the smaller End of their Eggs. The People so highly resented this Law, that our Histories tell us, there have been six Rebellions raised on that Account; wherein one Emperor lost his Life, and another his Crown. These civil Commotions were constantly fomented by the Monarchs of Blefuscu; and when they were quelled, the Exiles always fled for Refuge to that Empire. It is computed, that eleven Thousand Persons have, at several Times, suffered Death, rather than submit to break their Eggs at the smaller end. Many hundred large Volumes have been published upon this Controversy: But the Books of the Big–Endians have been long forbidden, and the whole Party rendered incapable by Law of holding Employments.”
Jonathan
Swift was born in
Lilliput seems to represent England, and its enemy Blefuscu is variously considered to represent either France or Ireland. Note that the phrase “little–endian” seems not to appear explicitly in the text of Gulliver’s Travels.