More on
Addressing Modes
Here
we review the material from the previous lecture and give other examples.
Modes
of interest here span quite a few architectures and might use inconsistent
notation.
We
begin with the idea of an Effective
Address, often denoted “EA” or “E.A.”
This basic idea facilitates understanding the function of any given
operation.
Consider
two basic operators: Load from memory and Store to memory
Load Register from Memory: R ¬ M[EA]
Store Register to Memory: M[EA] ¬ (R)
By definition of the term “Effective Address”, all
memory references use that address when accessing memory. M[EA] denotes the contents of the effective address.
Understanding
addressing modes then becomes equivalent to understanding how to calculate the
Effective Address.
We
begin with a simple mode, called “Direct Address” and then move to a few
addressing modes for which the term “Effective Address” is not appropriate.
We
then move to a series of increasingly complex addressing modes, ending with a
few actually used on commercial machines.
Calculation
of Effective Address
We
now consider how to calculate an effective address, given the ISA instruction.
We
begin with the format of a generic instruction referencing memory. The standard format includes an Address Field,
which is used in many address calculations.
Often it is the Effective Address, but again can be just part of that
address.
The
Boz–5 instruction format is as follows.
|
Bits |
31 – 27 |
26 |
25 – 23 |
22 – 20 |
19 – 0 |
|
Use |
Five–bit Opcode |
Indirect |
Destination or |
Index |
Address |
In general, the only
parts of the instruction that are used in computing the EA are
the
Address Field this contains an address, which may be
modified.
the Index
Register this contains the register used
as “array index”.
If
this field is 0, indexing is not used.
the
Indirect Bit this is used for
Indirect and Indexed–Indirect addressing.
If
this is 1, indirect addressing is used; otherwise not.
Instructions that do not use
an address field conventionally have that field set to 0.
Direct and
Immediate Addressing
Before
discussing the idea of an Effective
Address, let’s discuss instructions
for which the idea of an EA is not appropriate.
No
argument: HLT //
Stop the computer.
Immediate
Argument: LDI %R3, 2 // Load the value 2 into
R3.
ADDI
%R4, %R4, 1 // Increment R4
98%
of Load Immediate and Add Immediate use the values – 1, 0, and + 1.
Register–To–Register: ADD %R3, %R1, %R2 // R3 = R1 + R2
SUB
%R3, %R1, %R2 // R3 = R1 – R2
To clarify the difference
between direct and immediate addressing, consider these:
LDI %R5, 400 //
Load register R5 with the value 400; R5 ¬ 400.
LDR %R5, 400 //
Load register R5 with the contents of memory
//
location 400; R5 ¬ M[400].
EA = 400.
NOTE:
Many of my examples use hexadecimal notation; this example is ambiguous.
Direct and
Indirect Addressing
|
Opcode |
Registers |
Mode
Flags |
Address
Field |
In each of direct and
indirect addressing, the computation is simple:
Just copy the address field itself.
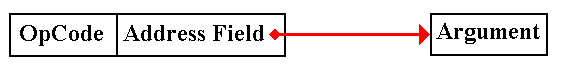
In
direct addressing, the address field
contains the address of the argument.
In indirect addressing, the address field contains the address of a pointer to the argument. Put another way, the contents of the memory
indicated by the address field contain the address of the argument.
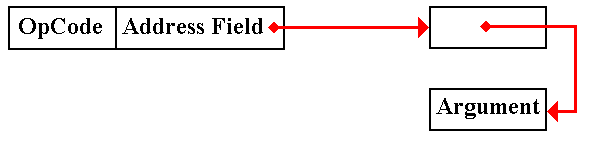
In
subroutine linkage, argument passing by preference basically uses indirect
addressing.
Direct and
Indirect Addressing (Example)
Consider
the following address map as an example for our addressing modes.
Z represents address 0x0A. Z == 0x0A and M[Z] =
5.
|
Address |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
10 |
11 |
|
Contents |
11 |
32 |
2C |
1E |
56 |
5 |
7A |
10 |
3 |
F |
E |
D |
8 |
Direct Addressing LDR %R1, Z
Effective Address: EA = Z Here
EA = 0x0A.
Effect: R1
¬ M[Z] Here R1 ¬ M[0x0A] or R1 = 5.
Indirect Addressing LDR %R1, *Z
Effective Address: EA
= M[Z] Here
EA = M[0x0A] = 5
Effect: R1
¬ M[EA]
= M [ M[Z] ]
Here
R1 ¬ M[0x05] or R1 = 11.
NOTE: The complexity of notation such as “R1 ¬ M[ M[X] ]” is one reason we
use
the Effective Address idea. Break the address computation into small
steps.
Indexed
Addressing
This
is used to support array addressing in all computers. Languages such as C and
C++ implement this directly using “zero based” arrays.
In
this mode, the contents of a general–purpose register are used as an index.
The
contents of the register are added to the address field to form the effective
address.
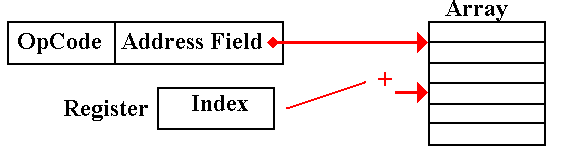
EA
= (Address Field) + (Register)
Although
we expect the index to be smaller than the value of the address, such
considerations are not profitable.
The
contents of the address field should be considered as having a different data
type from those of the register, which holds a signed integer.
Indexed
Addressing (Example)
LDR %R1, Z, 3 // Z indexed
by the general–purpose register R3.
Z represents address 0x0A. Z == 0x0A and M[Z] =
5. (R3) = = 4
|
Address |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
10 |
11 |
|
Contents |
11 |
32 |
2C |
1E |
56 |
5 |
7A |
10 |
3 |
F |
E |
D |
8 |
Effective address: EA = Z + (%R3) Here EA = 0x0A + 4 = 0x0E
Effect: R1
¬ M[EA]
= M[0x0E] or R1 = F
In
this, the most common, variant of indexed addressing we see Z as an array.
The first five elements of the array are placed in memory as follows:
|
Memory
Map |
0x0A |
0x0B |
0x0C |
0x0D |
0x0E |
|
Contents: |
Z[0] |
Z[1] |
Z[2] |
Z[3] |
Z[4] |
One Variant
of Indexed Addressing
Consider
the use of general purpose register %R0 as an index register.
LDR %R2, Z, 0
There are two possible interpretations of this
instruction.
1. Do not use indexing in computation of this
address. The effective address is
simply EA = Z and the mode is
really direct addressing.
2. Register R0 is identically 0; %R0 º 0. Use this
value to calculate the effective
address, EA = Z + (%R0) = Z + 0
= Z. The mode is the same as direct
addressing.
OUR MOTTO: If it acts
identically to direct addressing, it is direct addressing.
We shall use this fact to simplify the design of the
control unit.
Another
Variant of Indexed Addressing
LDR %R4, Z,
7 //
Address Z indexed by R7
But suppose Z = 0.
The format of the machine language instruction is:
|
31 |
30 |
29 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
23 |
22 |
21 |
20 |
19 – 0 |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
7 |
0x00000 |
||||
The
effective address is EA = Z + (%R7) = 0 + (%R7).
The register itself contains the address; this is register indirect addressing.
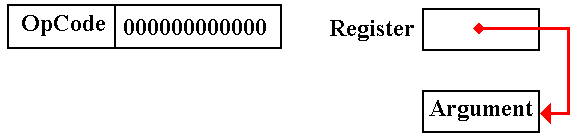
Based
Addressing
This
is quite similar to indexed addressing, so much so that it seems redundant.
This
mode arises from an entirely different consideration.
Indexed addressing basically supports the use of arrays.
Based
addressing supports the Operating
System in partitioning the user address space.
User addresses are mapped into physical addresses that cannot conflict.
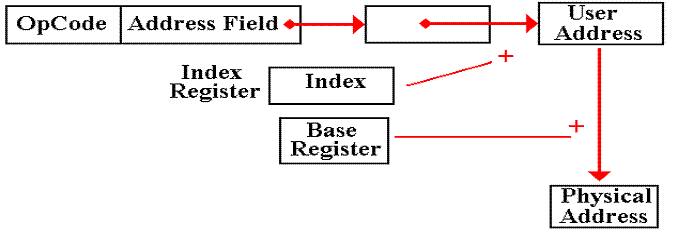
The Boz–5 uses the page
number in the PSR as a base register.
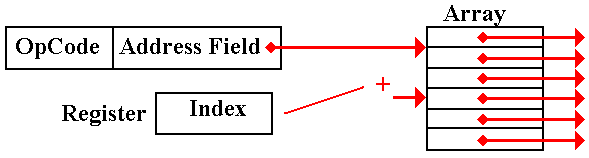
Indexed–Indirect
Addressing
This
is a combination of both modes.
Question: Which is done first?
Pre–Indexed Indirect: The indexing
is done first. We have an array of
pointers.
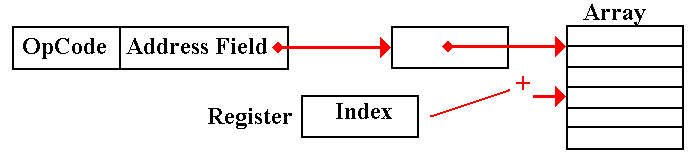
Post–Indexed Indirect: The indirect
is done first. We have a pointer to an
array.
Indexed–Indirect
Addressing (Example)
Let Z refer to address
0xA, so that M[Z] = = 0x05. Let (R3) = 0x07.
|
Address |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
10 |
11 |
|
Contents |
11 |
32 |
2C |
1E |
56 |
5 |
7A |
9 |
3 |
F |
E |
D |
8 |
Pre–Indexed Indirect: LDR
%R1, *Z, 3
Effective address EA = M[ Z + (R3) ] = M[0xA + 0x7]
=
M[ 0x11] = 0x08.
Effect R1¬ M[ M[Z + (R3)] ] or R1 ¬ M[0x08] or R1 ¬ 1E
Post–Indexed Indirect: LDR
%R1, *Z, 3
Effective address EA = M[ M[Z] + (R3) ] =
M[ M[0x0A] + 0x07]
=
M[0x05 + 0x07] = M[0x0C] = 0x09.
Effect R1 ¬ M[0x09] or R1 ¬ 0x56
Pre–Indexed
Indirect Addressing: Variant 1
Again, consider the use
of general–purpose register R0 as an index register.
Remember that this
register is set identically to 0; %R0 º 0.
Pre–Indexed Indirect: LDR
%R1, *Z, 0
Effective address EA = M[ Z + (R0) ] = M[Z]
Effect R1¬ M[ M[Z] ].
But this is just the indirect addressing, discussed above.
Again, this feature will
be used to simplify the control unit.
Pre–Indexed
Indirect Addressing: Variant 2
We now come to a more
unusual variant of pre–indexed indirect addressing.
Suppose the address part
is 0, Z = 0.
LDR %R4, *Z,
7 //
Address Z indexed by R7
|
31 |
30 |
29 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
25 |
24 |
23 |
22 |
21 |
20 |
19 – 0 |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
7 |
0x00000 |
||||
The Effective Address is
a bit unusual
Effective address EA = M[ Z + (R7) ] = M[0 + (R7)] =
M[(R7)]
Effect R1¬ M[ M[(R7)] ]
R7 contains the address
of a pointer. R7 is a pointer to a
pointer.

We
would have to make the control unit more complex to remove this addressing
mode.
Getting Rid
of Direct Addressing
We
now simplify our control unit by introducing a new register convention.
As
is common among many modern computers, we define a register zero, called R0
and demand that it be identically 0. Thus R0 º
0.
Stores
to register R0 are ignored. This
register cannot be changed.
Consider
two instructions
Load X, (R2) EA =
X + (R2) Indexed addressing
Load X, (R0) EA =
X + (R0) = X Really
direct addressing.
Consider
a typical address part of an instruction:
|
Mode Field |
Index Register |
Address Field |
There are two options for the
Index field.
More complex If zero, use direct addressing
If
not zero, use the register as an index register.
Less complex Use the given register as an index
register for indexed
addressing. If R0, then add 0 to the address field,
giving
essentially
direct addressing.
At
the microarchitecture level, we lose no efficiency in always adding the
register to form the address. We gain a
great deal by simplifying the address computation.
Double
Indirect Addressing: Use 1
Suppose a common data structure
that is used by a number of programs.
In modern systems, this could be a DLL (Dynamic Linked Library) module.
Each program contains a pointer
to this structure, used to access that structure.
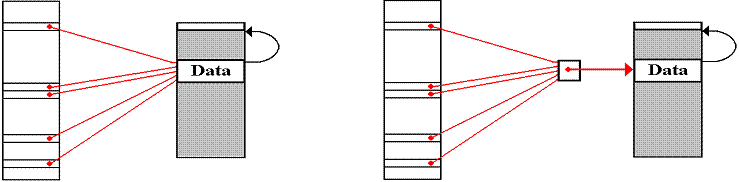
Singly indirect addressing, in
which the pointer is stored in every program, presents problems when the data
block is moved by the memory manager.
Every reference to that block must be found and adjusted.
In doubly indirect addressing,
all programs have a pointer to a data structure which itself is a pointer. When the data block is moved, only this one
pointer must be adjusted.
As an extra benefit, this
intermediate pointer can be expanded to a data structure containing an ACL
(Access Control List) and other descriptors for the data block.
This presents the beginning of a more secure operating system.
Double
Indirect Addressing: Use 2
The Operating System uses
double indirection to activate a device driver associated with a given I/O
device. For each type of I/O device, the
O/S stores the address of a
“device vector”, which contains the
actual address of the software to handle the device.
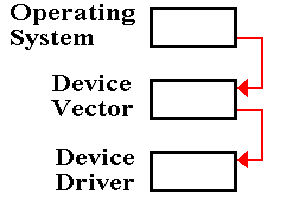
This arrangement allows the
operating system and the device drivers to be developed independently. The only fixed location is the address of
this device vector.
When the driver software is
loaded, the O/S places it in the memory location that is most convenient for
the current configuration and copies that start address into the address part
of the device vector. Double indirection
is then used to call the driver.
This is really a “vectored interrupt” mechanism,
described more fully in a later chapter.